CEX、DEX 套利剖析
作者:Atis E 来源:medium 翻译:善欧巴,比特币买卖交易网
本文着眼于 CEX/DEX 套利交易的机制,重点关注执行的 AMM 方面,旨在展示区块时间、区块基本费用以及参与这些交易的参与者(有限合伙人、搜索者等)之间的关系。它包括带有可用源代码的模拟结果。
人们普遍认为,CEX/DEX 套利交易创造了 DEX 交易量的很大一部分,甚至可能是该交易量的大部分。损失与再平衡 (LVR) 模型 1 是一种从理论角度量化和建模套利量的方法。
然而,它容易受到误解和误解。例如,一些研究 论文陈述(或暗示)这样的假设:套利交易的有限合伙人损失随着区块时间的平方根而增长。这来自于在理想化设置中对 LVR 进行建模。然而,实际运行模拟的作品(比如这个)通常揭示出较短区块时间的影响最小。我们如何协调这些不同的结果并弥合理论与实践之间的差距?
可以说,大部分差异来自于套利是一种两人零和游戏的假设,正如 LVR 研究中通常建模的那样。然而,这种假设在 EIP-1559 之后的世界中是无效的,因为那里的交易不可能是免费的。每笔套利交易不仅会在搜索者、构建者和提议者(SBP,如本文后面提到的)之间分配利润,还会根据套利时的区块空间需求燃烧一些 ETH。借用物理学术语,基本费用会在这个过程中引入摩擦。这种摩擦消除了很大一部分潜在交易,并减少了有限合伙人的收入。
1 — 就我个人而言,我更愿意将其称为 CVR(成本与再平衡),因为在现实世界的 DEX 中,不存在通过 LVR 准确量化损失的真实实体。相反,DEX 设计者和 LP 可以考虑的一个关键问题是他们所承受的理论 LRV 的百分比是多少,即 LVR 的一部分实际上是在 DEX 仅由套利交易者使用的模型中 LP 的预期损失。也就是说,我将在本文中坚持使用 LVR,以避免更多混乱。
价格行为示例
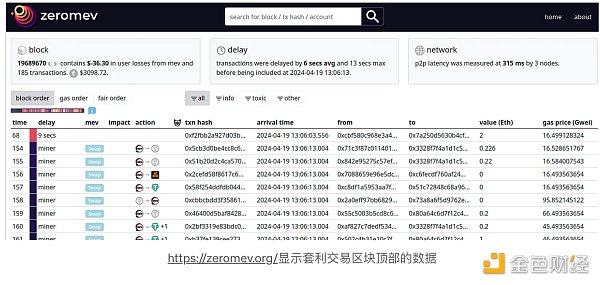
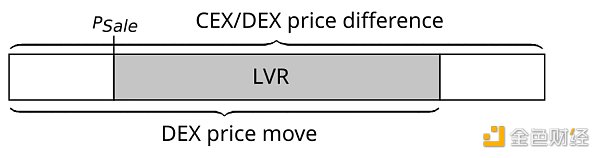
让我们详细研究一下套利机制。下图展示了 CEX 上的价格变化足以吸引套利后 DEX 池中的典型状态。
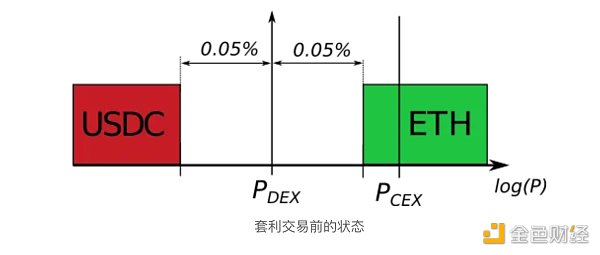
下图描绘了套利交易后的状态。DEX 价格已从P_Old转变为P_DEX ,并且 LP 以P_Sale价格出售其资产,该价格代表两个价格之间的几何平均值。新的DEX价格仍与CEX价格略有偏离,但仍处于非套利区域内。因此,除非 CEX 价格小幅上涨或大幅下跌以完全跨越非套利阈值,然后再超过一些,否则不会发生进一步的交易。
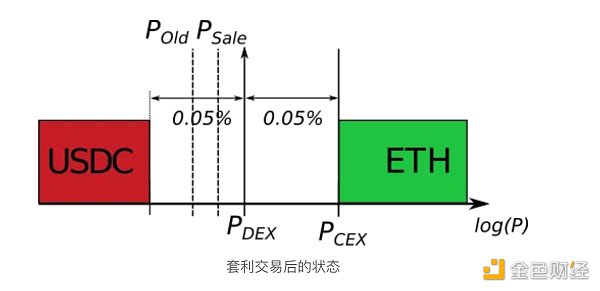
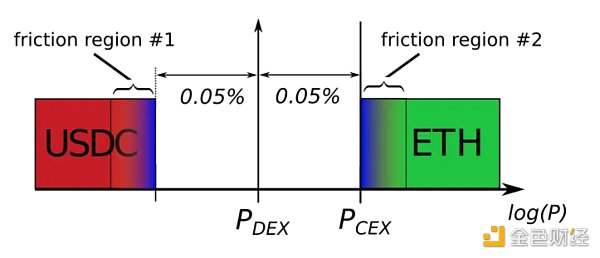
如果现在 CEX 价格上涨 0.001% 会发生什么?交易不会发生。这是因为,在矿池交换费用造成的非套利缺口的两侧,存在一个摩擦区域,该摩擦区域是由区块链的基本费用和其他因素造成的,包括 CEX 费用(如果有)、优先费和对区块提议者的贿赂、套利者的预测准确性和风险承受能力等等。
就本文而言,假设区块基本费用造成了大部分摩擦,而忽略了其他因素。基本费用产生的摩擦是套利者可以预测的,并且他们不太可能在减去下一个区块的预期基本费用后预期利润为负的情况下创建任何掉期。
单笔交易LVR分析
当 CEX 和 DEX 报价之间的差异足够超过池的掉期费率时,就会触发套利交易。但单笔套利交易实现的LVR与该价差并不成正比。相反,LVR 与 CEX 和 DEX 上的交易执行价格之间的差异成正比。假设CEX交易执行价格等于报价,但DEX交易执行价格为P_Sale,即交易前后报价的几何平均值。
此外,单笔交易LVR分布在三个实体中:
流动性提供者
搜索者、区块构建者和区块提议者(SBP)作为一个集体实体
ETH 持有者,受到交易中销毁的 ETH 的影响
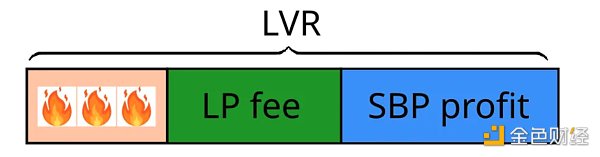
LP收取掉期费用,而SBP收取套利利润,这些利润随后在这三个参与者之间分配。综合搜索者-构建者主导套利市场也就不足为奇了,因为他们要应对利润分配中简化版的委托代理问题。
ETH持有者并不直接获得补偿,但由于通货紧缩压力,他们的ETH价值长期会小幅上涨。
高波动性增加了价格上涨的可能性,从而增加了套利交易。此外,它还使得预期的跳跃幅度更大。有限合伙人费用通常与波动性无关,导致当波动性上升时,有限合伙人的分配不公平。
通过比较单笔交易的LVR和该交易的LP费用,我们可以评估该交易对LP的公平性。在价格演变平稳、没有跳跃的情况下,LP费用几乎可以收回LVR,LP损失很小。然而,如果 DEX 到 CEX 的价差由于区块时间粒度或 CEX 上的实际价格不连续性而波动,则 LP 费用将小于 LVR,从而导致 LP 对于这种(理论上的)再平衡策略产生一些损失。
示例场景
让我们对 Uniswap v3 ETH/USDC 0.05% 池的范围内流动性进行建模。截至 2024 年 4 月,它拥有价值约 10 亿美元的虚拟资产,相当于约 1.5 亿美元的实物资产,流动性集中度为 6。如果我们希望即使在规模相对较小的情况下也能进行套利互换,那么拥有深厚的流动性至关重要。价格变化。
一个简单的 Uniswap v3 交换可能会消耗大约150,000 Gas,相当于每次交换的美元成本为 10 美元,假设合理的 22 gwei 基本费用成本和 3000 美元的 ETH/USDC 价格。在 DeFi 压力和高波动性时期,成本很容易增加数倍。
实施例1
假设 ETH 在 CEX 和 DEX 上的起始价格都是 3000 美元。
首先,让我们看看当 CEX 价格变化 +0.1% 时会发生什么。目前CEX价格为3003美元,处于非套利区域之外。套利者计算 DEX 目标价格P_T,由于矿池收取 0.05% 的费用,等于 3003 · 0.9995,并在 DEX 上将部分 USDC 换成 ETH,将 DEX 价格提高到目标价格。交换金额由池中的流动性L和(虚拟)储备x和y定义:
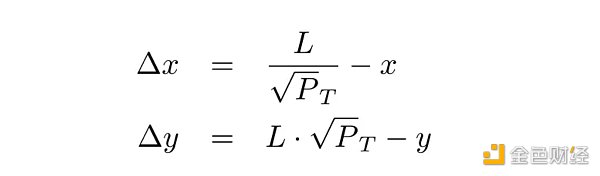
这将返回不含费用的金额,要获得含费用的输入金额,结果必须除以 0.9995(对于 0.05% 池)。
LVR 是根据 delta 和 CEX 价格P_C计算得出的:
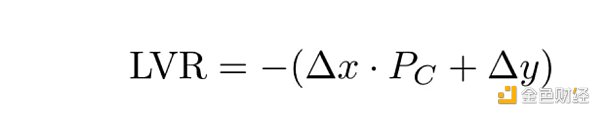
然后,LVR 分为 LP 费用部分、SBP 利润部分和区块基本费用,该费用不取决于交易的细节,除了其 Gas 成本:
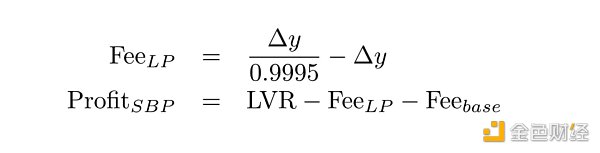

如果估计的 SBP 利润为正,则交易可能会发生,否则不会。
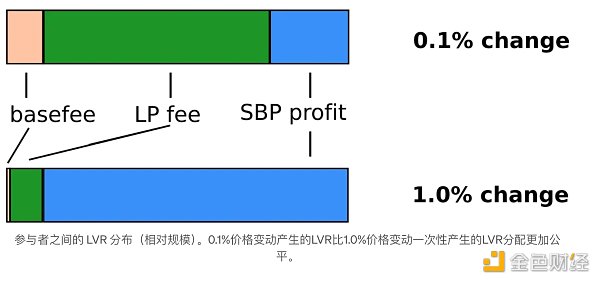
对于价值 1B 美元虚拟资产的示例池,掉期的 LVR 为 93.66 美元,LP 费用为 62.46 美元,导致理论单笔交易 LVR 的 33.3% 作为 LP 损失实现。大约三分之一的损失来自 10 美元的区块基本费。
实施例2
保持相同的假设,但让 CEX 价格变化 1%。
在这种情况下,有限合伙人确实获得了 1184.66 美元的令人印象深刻的费用。然而,单笔交易LVR增长更快,达到12406.47美元,这意味着LP损失占理论LVR的90%。
这表明有限合伙人的损失与价格变化呈超线性关系。价格上涨了 10 倍(0.1% vs 1.0%),但 LP 损失增加了 360 倍以上(31.19 美元 vs 11221.81 美元)。
实施例3
从前面的例子可以看出,如果有限合伙人能够逐步进行交易,而不是一次性进行全部交易,那么他们的境况会更好。
让我们考虑一个短区块世界,其中价格两次变化 +0.1%(即从 3000 美元到 3003 美元,然后到 3006 美元),以及一个长区块世界,其中价格一次变化 +0.2%。
LP 费用为 187.39 美元,两种情况相同。(这些交易是路径独立的,因为我们假设不复利费用。)但是,第二个的 LVR 更高。
具体来说:
对于短区块,累计LVR为343美元,LP损失为45.4%。
对于长区块,累计LVR为468美元,LP损失为60.0%。
实施例4
最后,让我们考虑一下振荡价格的例子。首先,价格变化 -0.1%,然后从起始价格增加到 +0.2%。在短区块世界中,有限合伙人能够进行两次交易,而在长区块世界中,有限合伙人无法交易价格下跌及其逆转,因为它们都发生在区块内。
结果是:
对于短区块,累计LVR为843美元,LP费用为312美元,LP损失为63.0%。
对于长区块,累计LVR为248美元,LP费用为187美元,LP损失为60.0%。
这个例子表明 LVR 是一个违反直觉的指标。在短区块世界中,矿池的交易量要高得多,收取的费用也相应更高。而且,最终价格是相同的,因此两个世界的无常损失是相等的。然而,在较长的区块世界中,实现的 LVR 以及通过 LVR 量化的 LP 损失都更高。
示例摘要
总结结果:
如果价格可以建模为 GBM 过程,那么总体而言,这两个模型都表明短区块世界可能是更可取的。
如果价格遵循其他模式,例如围绕均值波动,那么根据 LVR 模型,较短的区块将导致更糟糕的结果。
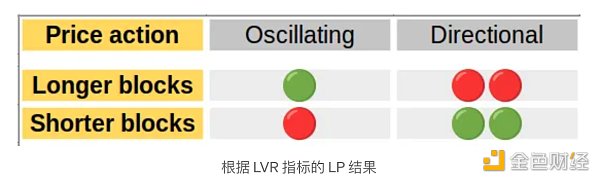
LP 结果总结如上图所示。
值得强调的是,从有限合伙人的角度来看,使用无常损失+费用作为衡量标准会产生截然不同的结果:
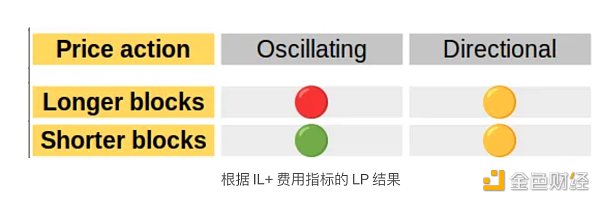
然而,我们知道,对于遵循 GBM 假设的易失性对,基于 IL 和 LVR 的模型最终应该收敛到相同的结果,因为 LVR 的期望值等于 IL 的期望值。我们需要超越迄今为止分析的具体案例。请参阅下一节!
模拟研究
下图显示了使用随机 GBM 模拟的 DEX 性能指标。模拟假设每年波动率为 50%,这对应于 12 秒区块的每日波动率约为 2.6%,每区块波动率为 0.03%。这就是ETH近年来的大概波动情况。
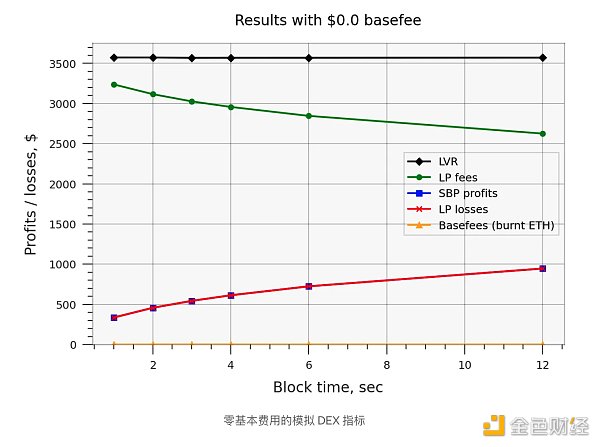
模拟运行了 3600 秒,由于巧合,LVR 大约为每秒 1 美元或每小时 3600 美元²。LP 的损失则在每小时 350 美元到 900 美元之间(每年 3 到 800 万美元)。需要明确的是,该理论模型不包括来自噪声/不知情交易者的任何 LP 费用,这些交易者的 LVR 预计为零,从而补偿套利交易的 LP 损失。
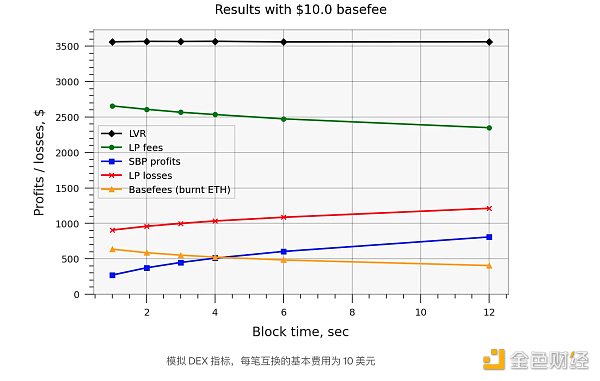
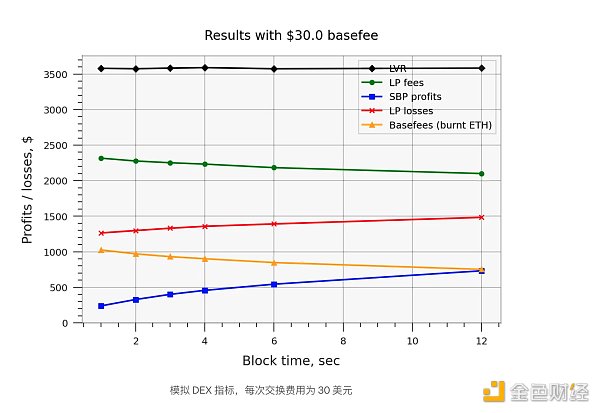
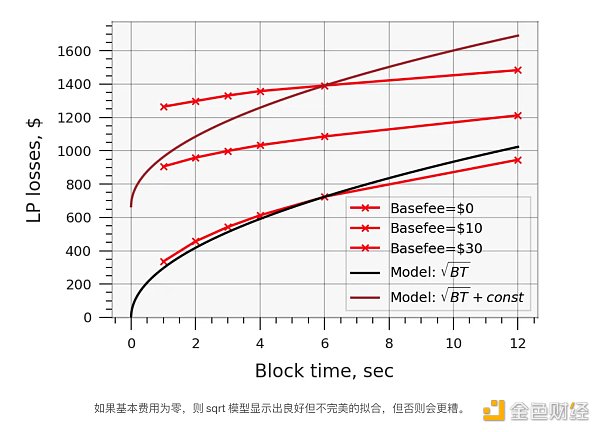
结果表明,当基本费用为零时,LP 损失确实可以通过函数sqrt(blocktime) + const精确建模(即不是通过其本身的平方根,因为即使对于短块,也存在与x轴的一些偏移) )。然而,在我们将 EIP-1559 基本费用引入模型后,这个结果不再成立,因为更频繁的交易也会消耗更多的 ETH,从而抵消了对 LP 费用的大部分积极影响 - 请参阅下面的结果。此外,更重要的是,基本费用成本增加了与x轴的恒定偏移。
² — 由于模拟所选择的设置,结果可用作主网上 Uniswap v3 USDC/WETH 0.05% 矿池的粗略且可能非常不准确的近似值。分析匹配并找出实证表现之间差异的最大原因可能是进一步研究的主题。
概括结果
推广到其他池。模拟结果特定于 USDC/ETH 0.05% 池,该池通常是 Uniswap v3 上流动性最强的波动性池。对于流动性较低的矿池,基本费用造成的摩擦的重要性将会增加。例如,假设 ETH/USDT 0.05% 池拥有 1/3 的流动性。那么该池的 10 美元基本费的结果将与 30 美元基本费的 USDC/ETH 池的结果相匹配。对于流动性较高的矿池(例如 USDC/USDT 和其他稳定货币对),摩擦也会类似地减少。
推广到其他链。该模型假设较短的块只是以不同的方式划分可用块空间,而不是添加更多块空间。如果区块时间的减少伴随着基本费用的成比例减少,模拟结果不会具有普遍性,并且看起来会非常不同。
复制理论结果
(这是一个技术性更强的部分,大多数读者可以跳过。)虽然我的模拟不能保证准确,但可以将它们与论文“存在费用的自动做市和套利利润”的结果进行比较。不同作品之间的设置/假设有两个主要差异:
该论文假设交易无摩擦——套利者没有基本费用或其他成本。
该论文假设区块时间呈泊松分布。
我没有重新设计 DEX 模拟以纳入非均匀的区块时间,而是设计了一个用于“快速”模拟的单独函数,该函数仅计算每个区块的交易概率,而不是其他指标。结果与论文非常吻合:
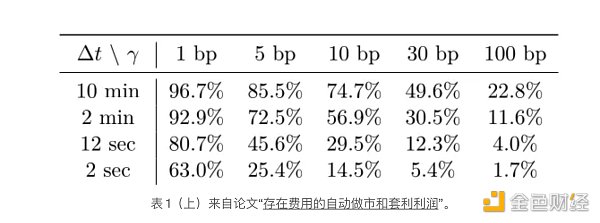
当函数更改为使用统一的块时间时,结果略有不同,但没有显着差异。完整 DEX 模拟的结果与快速模拟相当吻合,让人相信它的实施是正确的。(或者至少,具有相同的假设):
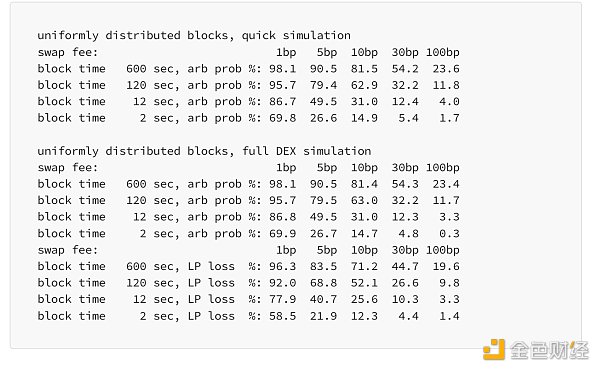
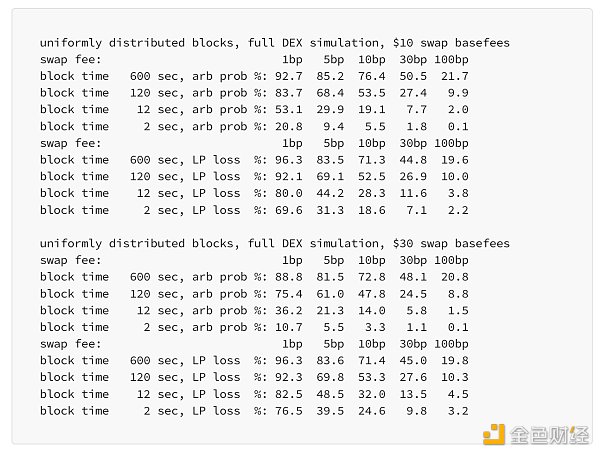
然而,当添加非零基本费用时,较短出块时间的积极影响会大大减少:
对区块链设计的影响
上面 DEX 性能指标图中的“LP 损失”曲线清楚地表明,LP 损失实际上并不与区块时间的平方根成比例增加,除非基本费用为零。这并不是一个新颖或意外的发现,而只是重申了交易更频繁会导致交易成本更高的原则。然而,鉴于 sqrt 时间模型已成为一种常见假设,它可能会受益于更广泛的传播。
仅挑选一个与该假设相冲突的显着结果:根据模拟结果,最好
以 120 秒的区块时间在链上的 30 bps 池中提供流动性,
而不是为了
以 2 秒的出块时间在链上的 5 bps 池中提供流动性
如果交易的基本费用等于 10 美元。有限合伙人的相对损失分别为 26.9% 和 31.3%。在现实世界中,5 个基点池当然可能更好,但前提是来自嘈杂/不知情的交易者有足够的交易量。
虽然较短的区块确实有利于有限合伙人,但其影响是有限的,并且不如其他因素(基本费用、流动性深度、矿池费用等级和其他潜在因素)显着。关于快速区块时间的更有说服力的论据可能来自交易者的角度——因为更快的确认可以改善交易用户体验——或者来自其他参与者,例如较小的区块构建者,他们将有更多机会在短区块环境中赢得提议者拍卖。然而,较短的出块时间也会带来明显的中心化风险:增加了网络验证器的网络带宽和延迟要求;增加加工要求;地理邻近性更加重要;整体设计偏向HFT。不用说,替代方案的存在可能会根据其演变重塑整个争论——例如转向 L2;向 L1 添加预先确认;或其他。
因此,我们可以将区块时间设计问题分为两部分:
L1 视角:去中心化、可信中立的设计对于以太坊和其他旨在与以太坊竞争的 L1 区块链来说绝对必要。无论它们有多重要,都不应该针对单个应用程序的性能进行过度优化。
L2/应用链视角:相反,L2 或应用链不需要针对通用应用程序定制其设计。L2 费用可能已经足够低,可以将基本费用造成的摩擦降至可以忽略不计的水平。如果情况并非如此,那么矛盾的是,从 EIP-1559 基本费用中免除 CEX/DEX 套利互换将使 DEX 用户受益。
概括
总结一下:
由于 EIP-1559 基本费用和其他因素,套利交易并非毫无摩擦。
因此,现实世界中 DEX 中的理论 LVR 分为三个实体:LP、ETH 质押者和作为集体实体的 SBP。
更渐进的价格变化导致这三个实体之间的 LVR 分配更加公平。
在交易成本较高的链上,相对于其他因素,改变区块时间只会略微增加有限合伙人的利润。
This paper focuses on the mechanism of arbitrage trading, focusing on the implementation aspect, aiming to show the relationship between the basic expenses of blocks, time blocks and the participants, limited partners and searchers who participate in these transactions. It includes the simulation results with available source code. It is generally believed that arbitrage trading has created a large part of the trading volume, and may even be a large part of the loss and rebalancing model of this trading volume. It is a kind of arbitrage that is quantified and modeled from a theoretical perspective. However, it is easy to be misunderstood and misunderstood. For example, some research papers state or imply that the loss of limited partners in the hypothetical arbitrage transaction increases with the square root of the block time. This comes from the works that are modeled in the idealized setting but actually run the simulation, such as this one, which usually reveals that the short block time has the least impact. How can we coordinate these different results and bridge the gap between theory and practice? It can be said that most of the differences come from arbitrage is a kind of two-person zero. And the assumption of the game is usually modeled in the research, however, this assumption is invalid in the later world, because the transactions there cannot be free. Each arbitrage transaction will not only distribute the profits between the searcher, the builder and the proposer as mentioned later in this paper, but also burn some borrowed physical terms according to the demand for block space during arbitrage, which will introduce friction in the process, which will eliminate a large part of potential transactions and reduce the income of limited partners. Personally, I prefer to call it cost and rebalancing, because in the real world, there is no real entity that quantifies losses accurately. On the contrary, a key question that designers can consider is what percentage of the theory they bear, that is, part of it is actually the expected loss in the model used only by arbitrage traders, that is to say, I will stick to it in this paper to avoid more confusion. Let's study the arbitrage mechanism in detail. The following figure shows. The price change on the market is enough to attract the typical state in the pool after arbitrage. The following figure depicts the state after arbitrage trading. The price has changed from to and its assets are sold at the price. This price represents the geometric average between the two prices. The new price is still slightly deviated from the price, but it is still in the non-arbitrage area. Therefore, unless the price rises slightly or falls sharply to completely cross the non-arbitrage threshold and then exceeds some, no further transactions will occur. What will happen if the price rises now, the transaction will not be issued. This is because there is a friction area on both sides of the non-arbitrage gap caused by the exchange fee of the mine pool, which is caused by the basic cost of the blockchain and other factors, including the prediction accuracy and risk tolerance of the arbitrageur if there is a priority fee for the fee and the bribe to the block proponent. For this purpose, it is assumed that the basic cost of the block causes most friction and ignores other factors. The friction caused by the basic cost is predictable by the arbitrageur and they are unlikely to be subtracted. Analysis of creating any swap single transaction when the expected profit of a block is negative after the expected basic cost; When the difference between the sum quotation and the swap rate of the pool is enough, the arbitrage transaction will be triggered, but the realization of a single arbitrage transaction is not proportional to the difference; on the contrary, it is proportional to the difference between the transaction execution price and the sum quotation, assuming that the transaction execution price is equal to the quotation, but the transaction execution price is the geometric average of the quotations before and after the transaction; in addition, the single transaction is distributed among the three entities. Providers, searchers, block builders and block proponents, as a collective entity holder, are affected by the destruction in the transaction, charging swap fees and collecting arbitrage profits, and these profits are then distributed among these three participants. It is not surprising that the comprehensive searchers and builders dominate the arbitrage market, because they have to deal with the simplified principal-agent problem in profit distribution, and the holders are not directly compensated, but their value will rise slightly for a long time due to deflationary pressure, and their high volatility has increased. In addition, it also makes the expected jump larger, which leads to the unfair distribution of limited partners when the volatility rises. By comparing the cost of a single transaction with that of the transaction, we can evaluate the fairness of the transaction pair. In the case of stable price evolution without jump, the cost can almost be recovered, and the loss is small. However, if the price difference is due to the time granularity of the block or the actual price discontinuity, However, the fluctuation will lead to some losses for this theoretical rebalancing strategy. Example scenario Let's model the liquidity within the pool. As of June, it has virtual assets worth about $100 million, which is equivalent to about $100 million in physical assets. The liquidity concentration is that if we want to carry out arbitrage swaps even in a relatively small scale, it is very important to have deep liquidity. A simple exchange may consume about the same amount. The dollar cost of each exchange is US dollars. Assuming that the reasonable basic cost and the price of US dollars can easily increase several times during the period of pressure and high volatility, the example assumes that the starting price of sum is US dollars. First, let's take a look at what will happen when the price changes. The current price is outside the non-arbitrage area for the US dollar. Arbitrators calculate the target price because the fees charged by the mine pool are equal to and partially replaced by raising the price to the target price. The exchange amount is changed from liquidity and virtuality in the pool. Reserves and definitions This will return the amount excluding fees. In order to obtain the input amount with fees, the result must be divided by the sum price for the pool, and then divided into the fee part, the profit part and the block basic fee. The fee does not depend on the details of the transaction, except its cost. If the estimated profit is a regular transaction, it will not be exchanged for the example pool of virtual assets with a value of US dollars. The fee of US dollars leads to about one-third of the theoretical loss of a single transaction. The loss comes from the block basic fee of US dollars. The example keeps the same assumption, but lets the price change. In this case, the limited partners do get the impressive fee of US dollars. However, the single transaction grows faster and reaches US dollars, which means that the loss accounts for the theory. This shows that the loss of the limited partners has a superlinear relationship with the price change, but the loss has doubled by more than US dollars. From the previous example, we can see that if the limited partners can trade gradually instead of all transactions at once, their situation will be better. Let's consider a short block world in which the price is two. 比特币今日价格行情网_okx交易所app_永续合约_比特币怎么买卖交易_虚拟币交易所平台
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。


















