零知识证明历久弥新创新涌现的原因是什么?
作者:LambdaClass;翻译:mutourend;Yiping,IOSG Ventures
Part.1 Insight
零知识证明历久弥新创新涌现的原因是什么?
原文来源于 https://blog.lambdaclass.com/our-highly-subjective-view-on-the-history-of-zero-knowledge-proofs/
1. 引言
零知识、简洁、非交互式知识证明(zk-SNARKs),是一种强大的密码学原语,允许证明者说服验证者某个陈述的正确性,而无需透露陈述以外的任何信息。由于其在可验证私人计算、计算机程序执行正确性证明和区块链扩展方面的应用,zk-SNARKs受到广泛关注。我们相信,正如我们在文章中描述的那样,zk-SNARKs将对塑造世界产生重大影响。zk-SNARKs涵盖了不同类型的证明系统,使用不同的多项式承诺方案、算术化方案、交互式预言机证明或概率可检验证明。但这些基本思想和概念可追溯至20世纪80年代中期。自比特币和以太坊推出以来,zk-SNARKs的发展大大加速,因为它们能够通过使用零知识证明(通常被称为此特定用例的有效性证明)进行扩展。zk-SNARKs在区块链可扩展性方面起着至关重要的作用。正如Ben-Sasson所述,近年来看到了加密证明的寒武纪爆发。每种证明系统都有优势和劣势,并且设计时都考虑到了特定的权衡。硬件、算法、新证明和工具的进步不断提高性能,也催生了新系统的诞生。这些系统中许多已投入使用,并且我们不断突破界限。我们是否会拥有适用于所有应用的通用证明系统,或者会有几种适用于不同需求的系统呢?我们认为一个证明系统能够统治所有其他系统的可能性很小,原因包括:
1)应用的多样性。
2)不同的限制类型(关于内存、验证时长、证明时长)。
3)对鲁棒性的需求(如果一个证明系统被破坏,还有其他证明系统)。
即使证明系统发生了很大变化,它们都提供了一个重要的特性:证明可被快速验证。拥有一个验证证明并可以轻松适应新证明系统的layer,解决了与更改base layer(如以太坊)相关的困难。本文将概述 SNARKs 的不同特征:
1)密码学假设:抗碰撞哈希函数、椭圆曲线上的离散对数难题、knowledge of exponent。
2)透明 vs 可信设置。
3)证明时长:线性 vs 超线性。
4)验证器时间:恒定时间、对数、次线性、线性。
5)proof size。
6)易于递归。
7)算术化方案。
8)单变量多项式 vs 多变量多项式。
本文将探讨 SNARKs 的起源、一些基本构建模块以及不同证明系统的兴起(和衰落)。本文无意对证明系统进行详尽的分析。相反,只关注那些对我们有影响的人。当然,这些发展只有通过该领域先驱者的伟大工作和想法才有可能实现。
2. 基础知识
零知识证明并不新鲜。定义、基础、重要定理、甚至重要协议都是从 20 世纪 80 年代中期开始制定的。用来构建现代 SNARKs 的一些关键思想和协议是在 20 世纪 90 年代提出的(sumcheck 协议),甚至是在比特币出现之前(2007 年的 GKR)。使用它的主要问题与缺乏强大的用例(互联网在 20 世纪 90 年代并不发达)以及所需的计算能力有关。
1)零知识证明:起源 (1985/1989)。
零知识证明领域随着Goldwasser、Micali 和 Rackoff 《The knowledge complexity of interactive proof systems》 论文出现在学术文献中。有关起源的讨论,可观看2023年1月视频ZKP MOOC Lecture 1: Introduction and History of ZKP。该论文引入了完倍性、可靠性和零知识性的概念,提供了quadratic residuosity 和 quadratic non-residuosity 的构造。
2)Sumcheck 协议 (1992)。
sumcheck协议由Lund、Fortnow、Karloff 和 Nisan于 1992 年Algebraic Methods for Interactive Proof Systems 论文提出。它是简洁交互式证明最重要的构建模块之一。它帮助我们将多变量多项式evaluate求和的要求减少到随机选择点的单个evaluation。
3)Goldwasser-Kalai-Rothblum (GKR) (2007)。
GKR协议(见论文Delegating Computation: interactive Proofs for Muggles)是一种交互式协议,其证明者根据电路的门数线性运行,而验证者则根据电路的大小亚线性运行。在协议中,证明者和验证者就depth为d dd的有限域的fan-in-two运算电路达成一致,其中layer d dd对应input layer,layer 0 00对应output layer。该协议从有关电路输出的声明开始,该声明被简化为对前一层值的声明。使用递归,可将其转换为对电路输入的声明,从而可轻松检查。这些reductions是通过 sumcheck 协议实现的。
4)KZG polynomial commitment scheme (2010)。
Kate、Zaverucha 和 Goldberg在 2010 年Constant-Size Commitments to Polynomials and Their Applications引入了使用双线性配对群的多项式承诺方案。承诺由单个群元素组成,承诺者可有效地打开对多项式的任何正确evaluation的承诺。此外,由于batching技术,可以对多个evaluations进行打开。KZG 承诺为几个高效的 SNARKs 提供了基本构建模块之一,如 Pinocchio、Groth16 和 Plonk。它也是EIP-4844的核心。要直观地了解batching技术,可参看Mina to Ethereum ZK bridge。
3. 使用椭圆曲线的实用SNARKs
SNARKs 的第一个实用构造出现于 2013 年。这些构造需要预处理步骤来生成证明和验证密钥,并且是特定于程序/电路的。这些密钥可能非常大,并且取决于各方不知道的秘密参数;否则,可伪造proofs。将代码转换为可证明的代码需要将代码编译为多项式约束系统。起初,这必须以手动方式完成,既耗时又容易出错。该领域的进步试图消除一些主要问题:
1)拥有更高效的证明者。
2)减少预处理量。
3)具有通用而不是电路特定的setups。
4)避免采用可信设置。
5)开发使用高级语言描述电路的方法,而不是手动编写多项式约束。
当前,使用椭圆曲线的实用SNARKs方案有:
1)Pinocchio (2013)
2)Groth 16 (2016)
3)Bulletproofs & IPA (2016)
4)Sonic, Marlin, and Plonk (2019)
5)Lookups (2018/2020)
6)Spartan (2019)
7)HyperPlonk (2022)
8)Folding schemes (2008/2021)
3.1 Pinocchio (2013)
Pinocchio(见论文Pinocchio: Nearly Practical Verifiable Computation)是第一个实用、可用的 zk-SNARK。SNARK 基于二次算术程序 (quadratic arithmetic programs,QAP)。证明大小最初为 288 字节。Pinocchio的工具链提供了从C代码到算术电路的编译器,并进一步转化为QAP。该协议要求验证者生成特定于电路的密钥。它使用椭圆曲线配对来检查方程。证明生成和密钥设置的asymptotics渐近与计算大小呈线性关系,验证时长与公共输入和输出的大小呈线性关系。
3.2 Groth 16 (2016)
Groth 2016年论文On the Size of Pairing-based Non-interactive Arguments引入了一种新的知识论证,提高了由R1CS 描述问题的性能。它具有最小的证明大小(仅三个群元素)和涉及三个pairings的快速验证。它还涉及获取结构化references字符串的预处理步骤。主要缺点是,待证明的每个程序都需要不同的可信设置,这很不方便。Groth16 曾用于 ZCash。详情也可参看博客An overview of the Groth 16 proof system。
3.3 Bulletproofs & IPA (2016)
KZG PCS 的弱点之一是它需要可信设置。Bootle等人2016年Efficient Zero-Knowledge Arguments for Arithmetic Circuits in the Discrete Log Setting 论文中引入了满足内积(inner product)关系的 Pedersen 承诺openings的有效零知识论证系统。内积证明系统有一个线性证明者,具有对数通信和交互,但具有线性时长验证。其还开发了一种不需要可信设置的多项式承诺方案。Halo 2 和 Kimchi 都采用了采用IPA PCS思想。
3.4 Sonic, Marlin, and Plonk (2019)
Sonic、Plonk和Marlin通过引入通用且可更新的结构化reference字符串,解决了 Groth16 中每个程序的可信设置问题。Marlin 提供了基于 R1CS 的证明系统,是 Aleo 的核心。
Plonk引入了一种新的算术化方案(后来称为 Plonkish),并对copy constraints使用grand-product check。Plonkish 还允许为某些操作引入专门的门,即所谓的定制门。多个项目都有 Plonk 的定制版本,包括 Aztec、ZK-Sync、Polygon ZKEVM、Mina’s Kimchi、Plonky2、Halo 2 和 Scroll 等。可参看博客All you wanted to know about Plonk。
3.5 Lookups (2018/2020)
Gabizon 和 Williamson 在 2020 年引入了plookup,使用grand product check来证明某个值包含在预先计算的值表中。尽管之前在Arya中提出了lookup arguments,但其构造需要确定lookups的multiplicities,效率较低。PlonkUp论文展示了如何将 plookup argument 引入 Plonk。这些lookup arguments的问题在于,它们迫使证明者为整个表支付费用,而与其查找次数无关。这意味着大型表的成本相当大,并且已投入了大量的精力来将证明者的成本降低到其使用的查找数量。
Haböck 引入了LogUp,它使用对数导数将乘积检查转换为倒数之和。LogUp 对于Polygon plonky2 ZKEVM(Beyond Limits: Pushing the Boundaries of ZK-EVM) 的性能至关重要,其需要将整个表拆分为多个 STARK 模块。这些模块必须正确链接,并跨表查找来强化此操作。LogUp-GKR的推出利用GKR协议来提高LogUp的性能。Caulk是第一个prover time与table size呈亚线性关系的lookup argument,其预处理时长为O ( N log N )且storage为O ( N ) ,其中N为table size。随后出现了其他几个方案,如Baloo、flookup、cq和caulk+。Lasso提出了多项改进,避免在表具有给定结构时对其进行commit。此外,Lasso 的证明者只为查找操作访问的表条目付费。Jolt利用 Lasso 通过查找来证明虚拟机的执行情况。
3.6 Spartan (2019)
Spartan为使用 R1CS 描述的电路提供了 IOP,利用多变量多项式和sumcheck协议的属性。使用合适的多项式承诺方案,它会产生带有线性时长prover的透明 SNARK。
3.7 HyperPlonk (2022)
HyperPlonk基于使用多变量多项式的 Plonk 思想而构建。它不依赖于商来检查约束的执行情况,而是依赖于sumcheck协议。它还支持high degree约束,而不会损害证明者的运行时间。由于它依赖于多变量多项式,因此无需执行 FFT,且证明者的运行时间与电路尺寸呈线性关系。HyperPlonk 引入了适合较小域的新permutation IOP 和基于sumcheck的batch opening协议,这减少了prover的工作量、证明大小和验证者的时间。
3.8 Folding schemes (2008/2021)
Nova引入了folding方案的思想,这是一种实现增量可验证计算(IVC)的新方法。IVC 的概念可以追溯到Valiant,其展示了如何将2个长度为k kk证明,合并为,一个长度为k kk的证明。其思想为,可通过递归证明,来证明由step i ii到step i + 1 i+1i+1的执行是正确的,且验证由step i − 1 i-1i−1到step i ii的过渡proof是正确的,从而证明任何长时间运行的计算。
Nova 可以很好地处理uniform computations;后来随着Supernova的引入,被扩展到处理不同类型的电路。Nova 使用 R1CS 的宽松版本,并在友好的椭圆曲线上工作。使用友好的曲线cycles(如,Pasta曲线)来实现 IVC 也被用在 Pickles 中,Pickles 是 Mina 的主要基础模块,以实现简洁的状态。然而,folding的思想与递归 SNARK 验证不同。累加器的思想与batching proofs的概念有更深入的联系。Halo引入了累加的概念作为递归证明组合的替代方案。Protostar为Plonk提供了non-uniform IVC方案,支持high-degree gates和vector lookups。
4. 使用抗碰撞哈希函数的SNARKs
大约在Pinocchio开发的同时,出现了一些生成电路/算术方案的想法,可以证明虚拟机执行的正确性。尽管开发虚拟机的算术可能比为某些程序编写专用电路更复杂或效率更低,但它提供了一个优点,即任何程序,无论多么复杂,都可以通过证明它在虚拟机中正确执行来证明。TinyRAM 中的想法后来随着 Cairo vm 和后续虚拟机(如 zk-evms 或通用 zkvms)的设计而得到改进。使用抗碰撞哈希函数消除了对可信设置或使用椭圆曲线运算的需要,但代价是更长的proofs。
1)TinyRAM (2013)
在SNARKs for C中,开发了一个基于 PCP 的 SNARK,用于证明 C 程序执行的正确性,该程序被编译为 TinyRAM(精简指令集计算机)。该计算机采用哈佛架构,具有字节级可寻址随机存取存储器。利用非确定性,电路的大小与计算大小呈拟线性quasilinear关系,从而有效地处理任意和数据相关的循环、控制流和内存访问。
2)STARKs (2018)
STARKs是由 Ben Sasson 等人于2018年提出。其实现的proof size为O(log2n),且具有快速证明者和验证者,不需要可信设置,并且被认为是后量子安全的。其首先由 Starkware/Starknet 与 Cairo 虚拟机一起使用。其关键部件包括:
代数中间表示 (AIR)
和FRI 协议(Fast Reed-Solomon Interactive Oracle Proof of Proximity)。
STARKs也被其他项目(Polygon Miden、Risc0、Winterfell、Neptune)使用,或对其的一些改编(ZK-Sync 的 Boojum、Plonky2、Starky)。
3)Ligero (2017)
Ligero引入了一个证明系统,其 proof size为O(根号n),其中n为circuit size。它将多项式系数排列成矩阵形式并使用线性码linear codes。
Brakedown建立在 Ligero 的基础上,并引入了与域无关的多项式承诺方案的思想。
5. ZKP的一些新进展
在生产中使用不同的证明系统显示了每种方法的优点,并带来了新的发展。如,plonkish算术化提供了一种简单的方法来包含自定义门和lookup arguments;FRI 作为 PCS 表现出了出色的性能,领先于 Plonky。同样,在 AIR 中使用grand product check(导致带有预处理的随机化AIR)提高了其性能并简化了内存访问arguments。基于哈希函数的承诺已经流行起来——基于硬件中哈希函数的速度或引入新的 SNARK 友好哈希函数。
1)新的多项式承诺方案(2023)
随着基于多变量多项式的高效 SNARK(如 Spartan 或 HyperPlonk)的出现,人们对适合此类多项式的新承诺方案越来越感兴趣。Binius、Zeromorph和Basefold都提出了新的形式来致力于多线性多项式。Binius 具有零开销来表示数据类型的优点(而许多证明系统使用至少 32 位域元素来表示单个bit)并在binary域上工作。Binius承诺基于Brakedown,其设计目的是与域无关。Basefold 将 FRI 推广到 Reed-Solomon 以外的代码,从而形成与域无关的 PCS。
2)Customizable Constraint Systems(CCS) (2023)
CCS概括了 R1CS,同时捕获 R1CS、Plonkish 和 AIR 算术,无需任何开销。将 CCS 与 Spartan IOP 结合使用会产生 SuperSpartan,它支持high-degree约束,而无需证明者承担随约束degree而扩展的加密成本。特别是,SuperSpartan 为带有线性时间prover的 AIR 生成 SNARK。
6. 结论
本文描述了 SNARK 自 20 世纪 80 年代中期推出以来的进步。计算机科学、数学和硬件的进步,加上区块链的引入,催生了新的、更高效的 SNARK,为许多可以改变我们社会的应用程序打开了大门。研究人员和工程师根据自己的需求提出了对 SNARKs 的改进和调整,重点关注证明大小、内存使用、透明设置、后量子安全、证明者时间和验证者时间。
虽然最初有两条主线(SNARK 与 STARK),但两者之间的界限已经开始淡化,试图结合不同证明系统的优点。如,将不同的算术方案与新的多项式承诺方案相结合。可预期,新的证明系统将继续兴起,性能也随之提高,而对于一些需要一些时间适应的系统来说,将很难跟上这些发展,除非可轻松地使用这些工具,而无需更改一些核心基础设施。
Part.2 投融资事件
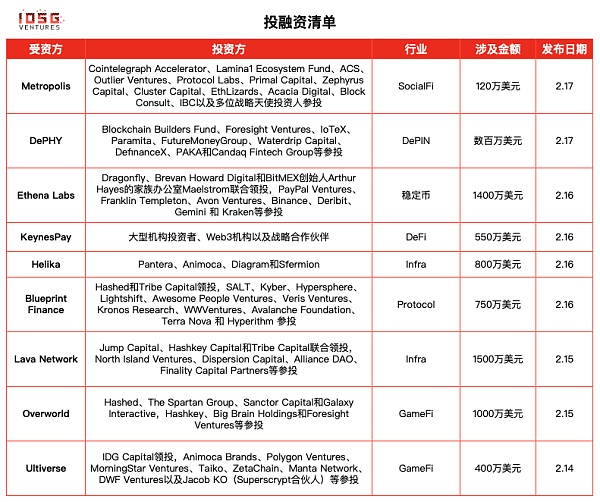
Web3数字身份初创公司Metropolis完成120万美元融资
* SocialFi
Web3数字身份初创公司Metropolis宣布完成120万美元融资,Cointelegraph Accelerator、Lamina1 Ecosystem Fund、ACS、Outlier Ventures、Protocol Labs、Primal Capital、Zephyrus Capital、Cluster Capital、EthLizards、Acacia Digital、Block Consult、IBC以及多位战略天使投资人参投。据悉Metropolis即将进行公开代币销售,并公布代币经济学和产品开发路线图。
DePIN基础设施DePHY完成种子轮融资
* DePIN
DePIN基础设施DePHY完成数百万美元种子轮融资,估值达4000万美元。Blockchain Builders Fund、Foresight Ventures、IoTeX、Paramita、FutureMoneyGroup、Waterdrip Capital、DefinanceX、PAKA和Candaq Fintech Group等参投,所筹集资金将用于开发者社区和平台项目的扩大及运营。此外,DePHY还将在Solana上部署可信DID(去中心化设备身份)解决方案,并在最近获得了Solana基金会的资助。
以太坊稳定币开发商Ethena Labs完成1400万美元战略轮融资
* 稳定币
以太坊稳定币USDe开发商Ethena Labs宣布完成1400万美元战略轮融资,投后估值达3亿美元。Dragonfly、Brevan Howard Digital和BitMEX创始人Arthur Hayes的家族办公室Maelstrom联合领投,PayPal Ventures、Franklin Templeton、Avon Ventures、Binance、Deribit、Gemini 和 Kraken等参投。该轮融资于去年12月底开始,本周结束。据此前消息,Ethena去年完成了600万美元的种子轮融资,Hayes通过家族办公室Maelstrom参投。Hayes也是Ethena的创始顾问。
加密支付平台KeynesPay完成550万美元Pre-Seed轮融资
* DeFi
数字资产金融服务集团Keynes Group宣布旗下第三方支付平台 KeynesPay完成550万美元Pre-Seed轮融资,投前估值超5000万美元投前估值。新增投资方包括大型机构投资者、Web3机构以及战略合作伙伴。本轮融资将用于深化KeynesPay在虚拟资产行业的支付生态布局,加快支付持牌业务产品多元化建设,推进集团在全球范围内合规和创新发展。据悉,Keynes Group核心业务还包括专门投资区块链技术和数字资产的全球资产管理公司Keynes Capital、全球比特币矿场矿机服务提供商Keynes Pool、链上社交平台KeChat以及Web3全球教育平台和社交网络Keynes IE。
Web3数据分析和基础设施服务公司Helika完成800万美元A轮融资
* Infra
为传统及Web3游戏提供数据分析和基础设施服务的公司Helika宣布已完成800万美元A轮融资,投资方包括Pantera、Animoca、Diagram和Sfermion。Helika的产品和服务套件以人工智能为驱动,能够整合多链、社交媒体和游戏的数据,并转化为游戏工作室可用以提高用户获取、留存和参与度的可操作见解,从而推动盈利增长。
Blueprint Finance完成750万美元融资,Hashed和Tribe Capital领投
* Protocol
链上信用协议Blueprint Finance宣布完成了750万美元的融资,此轮融资由Hashed和Tribe Capital领投,SALT、Kyber、Hypersphere、Lightshift、Awesome People Ventures、Veris Ventures、Kronos Research、WWVentures、Avalanche Foundation、Terra Nova 和 Hyperithm 参投。旨在解决加密货币市场的清算问题。Blueprint Finance的旗舰产品是Concrete Protocol,这是一个专门为链上债务和信贷设计的应用链,旨在提供更高的收益、清算保护以及跨DeFi的高级预测功能,首先从货币市场开始实施。
模块化区块链Lava Network完成1500万美元种子轮融资
* Infra
模块化区块链基础设施开发商Lava Network完成1500万美元种子轮融资,Jump Capital、Hashkey Capital和Tribe Capital联合领投,North Island Ventures、Dispersion Capital、Alliance DAO、Finality Capital Partners等参投。来自Celestia、Cosmos、StarkWare、Filecoin和其他区块链生态系统的的高管也参与了本轮融资。Lava计划在今年上半年推出主网。目前Lava有26名员工,其中20人是区块链工程师。
链游工作室Overworld完成1000万美元种子轮融资,Hashed等领投
* GameFi
链游工作室Overworld今日宣布已在种子轮融资中筹集到1000万美元。领投的投资者包括Hashed、The Spartan Group、Sanctor Capital和Galaxy Interactive,Hashkey、Big Brain Holdings和Foresight Ventures等参投。该笔资金将直接用于游戏的创作, Overworld 目前也正在工作室招聘多个角色。该工作室正在开发其首款游戏,暂时命名为Overworld,这是一款基于Xterio代币运作的Web3免费动作角色扮演游戏,具有动漫风格的艺术设计。
Web3游戏平台Ultiverse完成400万美元战略轮融资,IDG Capital领投
* GameFi
AI驱动的Web3游戏制作和发布一站式平台Ultiverse完成400万美元战略轮融资,IDG Capital领投,Animoca Brands、Polygon Ventures、MorningStar Ventures、Taiko、ZetaChain、Manta Network、DWF Ventures以及Jacob KO(Superscrypt合伙人)等参投。Ultiverse于2022年成立,是一个基于AI的Web3游戏制作和发行一站式平台,团队由游戏、技术和区块链项目专家组成。截至2023年12月,Ultiverse的注册用户已超过730万名,月活跃用户超过83万人。上一轮的投资方包括Binance Labs、红杉资本、DeFiance Capital、Emirates Consortium、MorningStar Ventures、GSR Ventures、Foresight Ventures等,投后估值达到1.5亿美元。
Part.3 IOSG投后项目进展
Coinbase向Bitcoin Core开发组织Brink捐赠360万美元
* DEX
Bitcoin Core开发组织Brink透露其已从加密交易平台Coinbase旗下支付平台GiveCrypto获得360万美元赠款,将用于全部用于Brink工程师及比特币开源开发工作上。
Filecoin宣布与Solana进行集成
* Infra
Filecoin今日发推文宣布与Solana进行集成,旨在摆脱中心化存储解决方案,并提高Solana区块链可靠性和可扩展性。Solana正在利用Filecoin使基础设施提供商、探索者、索引编制者以及任何需要历史访问的人都能更方便地访问和使用其区块历史。
Offchain Labs已在Arbitrum社区开启ArbOS 20 Atlas AIP提案投票
* Layer2
Arbitrum开发商Offchain Labs宣布已在Arbitrum社区提交ArbOS 20 Atlas AIP提案并已开启链上投票,该AIP提议支持以太坊Dencun,包括EIP-4844,以及批量海报改进,投票将于3月1日结束。
Stacks总锁仓价值突破1亿美元
* Payment
比特币Layer2网络Stacks推特发文宣布其总锁仓价值(TVL)已突破1亿美元,目前为1.12亿美元。
SyncSwap推出基于zkSync的404 Wrapper,实现ERC-721 NFT与ERC404代币互换
* Layer2
基于 zkSync 的去中心化交易平台 SyncSwap 宣布推出受 ERC404 启发的 SyncSwap 404 Wrapper,允许将现有的 ERC-721 NFT 封装成 ERC404 可替代封装代币。404 Wrapper 是 SyncSwap 的公共产品,在完全无需许可和开源的基础上运行,封装和解封 NFT 不收取任何费用。LIBERTAS OMNIBUS 是 zkSync 团队的一个实验性 NFT 项目。
Mina:与交易所和托管机构进行主网升级的封闭测试正在进行
* Layer 1
轻量级区块链协议 Mina Protocol 公布 Testworld Mission 2.0 的最新消息以及 Mina 主网主要升级的进展:Mina 开发团队 O(1) Labs 发布了第一个Berkeley 候选版本 RC1,此版本合并了之前 Testworld 2.0 Rampup版本的所有修复和发现。目标在测试网络环境中复制流程并设计升级机制的 Track 4 工作仍在继续,与交易所和托管机构进行的封闭测试正在进行中,并将贯穿整个 Track 4。
Part.4 行业脉搏
Connext已在Base上线,用户将可通过EigenLayer再质押原生ETH
* Layer 2
Layer2互操作性协议Connext宣发已在Base上线。Renzo Protocol 用户将可在Base上通过EigenLayer再质押原生ETH,而无需与以太坊交互。此外,用户还可获得ezPoints和EigenLayer再质押积分。
以太坊最新ACDE会议:讨论Dencun升级的主网激活准备和多项EIP
* Ethereum
Galaxy研究副总裁ChristineKim发文总结第181次以太坊核心开发者执行层会议(ACDE),会议讨论了Dencun升级的主网激活准备和多项以太坊改进提案(EIP)。其中包括为Pectra升级提议的EIPs,以及两项追溯性EIP,EIP 7610和7523,旨在修改智能合约创建规则和禁止空账户的存在。开发者还同意将EIP 2537,即添加BLS12-381曲线预编译,包含在Pectra中。Dencun升级的影子分叉准备工作正在进行中,目标是在3月13日前完成主网激活。此外,会议上讨论了Pectra升级的其他技术提案,包括提高外部拥有账户(EOAs)的智能合约功能,分配智能合约地址和存储槽的气体成本,以及支持无状态客户端的提案。开发者计划在下一次ACDE会议前,就所有账户抽象化和EVM相关代码更改进行详细讨论,并强调了确定Pectra升级时间线的重要性。
Polygon即将推出AggLayer v1主网,采用零知识证明促进链间互操作性
* Layer1
Polygon宣布,其最新的聚合层技术解决方案AggLayer v1主网即将推出。该技术旨在通过零知识证明(ZK证明)技术实现不同区块链之间的连接,从而支持跨链流动性的统一和安全。AggLayer的设计目标是为开发者提供一个平台,使他们能够轻松地将各种区块链网络连接起来,以实现流动性的统一管理。此外,AggLayer还将确保连接的链条—无论是模块化链还是整体式链,包括Polygon生态系统内的链条—都能享有统一的安全保障。作为Polygon网络下一代迭代,即Polygon 2.0的核心组成部分,AggLayer与传统的互操作性解决方案不同。它将通过聚合所有连接链条的ZK证明,提供一个更加高效和安全的互操作平台。
PlayDapp:PLA代币合约遭黑客攻击,PlayDapp持有的所有PLA将被强制转移至新的安全钱包
* GameFi
区块链游戏平台PlayDapp在推特发文称,PLA代币合约已遭黑客攻击,并已铸造额外的PLA代币。PlayDapp已直接通知所有交易平台合作伙伴,并与他们合作暂停交易及解决未经授权的代币问题。由于已确认影响PLA的安全漏洞,PlayDapp正在采取行动保护PLA资产,将所有PlayDapp持有的PLA强制转移到新的安全钱包,其中包括锁定和解锁的资产。据Cyvers Alerts监测,PlayDapp遭黑客攻击,攻击者的地址被添加为铸币者,铸造2亿枚PLA代币(价值3100万美元),目前这些PLA代币已分发到各个地址,其中价值590万美元的部分被盗PLA代币已转入Gate平台。
What is the reason why the author translated the zero-knowledge proof for a long time? The original text comes from the introduction. Zero-knowledge concise non-interactive knowledge proof is a powerful cryptographic primitive that allows the prover to convince the verifier of the correctness of a statement without revealing any information other than the statement. Because of its application in verifying the correctness of the execution of private computing computer programs and blockchain expansion, we believe that it will have a great impact on shaping the world as we described in the article. The great influence covers different types of proof systems using different polynomial commitment schemes, arithmetical schemes, interactive Oracle proof or probabilistic testable proof, but these basic ideas and concepts can be traced back to the mid-1900s, and their development has been greatly accelerated since the introduction of Bitcoin and Ethereum, because they can be extended by using zero-knowledge proof, which is usually called the validity proof of this specific use case, and play a vital role in blockchain scalability, as mentioned in recent years. In order to prove the CAMBRIAN explosion of encryption, each proof system has advantages and disadvantages, and the design has taken into account the specific trade-offs. The continuous improvement of hardware algorithms, new proofs and tools has also given birth to new systems. Many of these systems have been put into use and we are constantly breaking the boundaries. Will we have a universal proof system suitable for all applications or will there be several systems suitable for different needs? We think it is possible that one proof system can dominate all other systems. The reasons for the small nature include the diversity of applications, different types of restrictions on memory verification duration, and the need for robustness. If a proof system is destroyed, there are other proof systems, which all provide an important feature proof that can be quickly verified even if the proof system has changed greatly. Having a proof can easily adapt to the new proof system, which solves the difficulties related to changes such as Ethereum. This paper will outline the different characteristics of cryptography hypothesis anti-collision hash function ellipse. Discrete Logarithm Problem on Circular Curve Transparent and Trusted Proving Duration Linear Superlinear Verifier Time Constant Time Linear Easy Recursive Arithmetic Scheme Univariate Polynomial Multivariate Polynomial This paper will discuss the origin, some basic building blocks and the rise and decline of different proof systems. This paper has no intention to make a detailed analysis of the proof systems, but only pays attention to those who have an influence on us. Of course, these developments can only be achieved through the great work and ideas of pioneers in this field. It's not new to define the basic knowledge. Important theorems and even important protocols have been formulated since the mid-1990 s to build some key ideas and protocols in modern times. The protocols were put forward in the 1990 s, even before the emergence of Bitcoin. Its main problems are related to the lack of powerful use cases, the underdeveloped Internet in the 1990 s and the required computing power. The origin of zero-knowledge proof and the field of zero-knowledge proof have appeared in academic literature with the emergence of papers. The discussion on the origin can be watched in the video of the year and month. This paper introduces the concepts of perfect ploidy reliability and zero knowledge, and provides the protocol for the construction of sum. It is proposed by the paper in 2000 that it is one of the most important building blocks for concise interactive proof. It helps us reduce the requirement of multivariate polynomial summation to a single protocol at random selection points. See the paper, which is an interactive protocol. The prover runs linearly according to the number of circuits, while the verifier runs sublinear according to the size of circuits. And the verifier reached an agreement on the finite field operation circuit, in which the statement corresponding to the protocol was simplified from the statement of the output of the relevant circuit to the statement of the value of the previous layer, which can be converted into the statement of the input of the circuit by recursion, so that it can be easily checked that these are realized through the protocol and the polynomial commitment scheme using bilinear pairing groups was introduced in, and the commitment made by a single group element can effectively open any correct commitment to the polynomial. In addition, due to technology, The promise of opening multiple programs provides one of the basic building blocks for several high efficiency, such as and it is also the core. To intuitively understand the technology, please refer to the practical first practical construction using elliptic curves. These constructions need preprocessing steps to generate proof and verification keys, and these keys are specific to program circuits. These keys may be very large and depend on secret parameters unknown to all parties, otherwise they can be forged. To convert the code into provable code, it is necessary to compile the code into polynomials. At first, the beam system must be completed manually, which is time-consuming and error-prone. The progress in this field tries to eliminate some main problems. It has a more efficient prover to reduce the amount of preprocessing. It is universal rather than circuit-specific. It avoids using trusted settings to develop a method of describing circuits in high-level languages instead of manually writing polynomials to constrain the current practical scheme of using elliptic curves. See the paper. It is the first practical and available tool chain based on quadratic arithmetic program to prove that the size is originally bytes. From the code to the compiler of arithmetic circuit and further into this protocol, the verifier is required to generate a circuit-specific key. It uses elliptic curve pairing to check the equation to prove that the asymptotic of generation and key setting is linear with the calculation size, and the verification time is linear with the size of common input and output. In 2000, the paper introduced a new knowledge demonstration, which improved the performance of describing the problem. It has the smallest proof size of only three group elements and involves three rapid verification. It also involves obtaining knots. The main disadvantage of the preprocessing step of constructing character strings is that each program to be proved needs different trusted settings, which is inconvenient. It has been used for details and can also be seen in blogs. One of the weaknesses is that it needs trusted settings. In 2001, an effective zero-knowledge demonstration system that meets the commitment of inner product relationship was introduced into the paper. The inner product proof system has a linear prover with logarithmic communication and interaction but has linear duration verification. It also developed a polynomial commitment scheme that does not need trusted settings and adopted both. By thinking and introducing universal and renewable structured character strings, the problem of trustworthy setting of each program in the program is solved, which provides a proof system based on. The core of the system introduces a new arithmetical scheme, which is later called and allows the introduction of special doors for some operations, namely the so-called custom doors. The customized versions of many projects, including and so on, can be found in blogs and introduced in to prove that a certain value is included in the pre-calculated value table. Although it was put forward in the table before, its structure needs to be determined. The paper shows how to introduce these. The problem is that they force the prover to pay for the whole table. 比特币今日价格行情网_okx交易所app_永续合约_比特币怎么买卖交易_虚拟币交易所平台
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。


















