模块化 vs. 单体化架构已死
区块链可扩展性:水平扩展与垂直扩展的对比
作者:Avi Zurlo
编译:Block unicorn
近年来,随着Rollups技术的兴起,区块链的可扩展性问题一直集中在模块化与单体化的争议上。这种二元对立最初是一种有用的思维模式,用来推断区块链的可扩展性,但现在,它已经不能满足我们的需求。
那么,有哪些替代方案呢?
本文将探讨水平扩展与垂直扩展作为区块链可扩展性的基本框架,并解释采用水平扩展与垂直扩展的优劣。
理解模块化与单体化
首先,我们来定义一下:
模块化链将区块链的核心功能分解为不同的层。
单体化链将所有核心功能集成到单一、相互连接的层中。
我们可以将“层”看作是“机器”-单体化链有一个节点来执行所有任务,而模块化链有多个(2-3个)全节点来执行不同的任务。
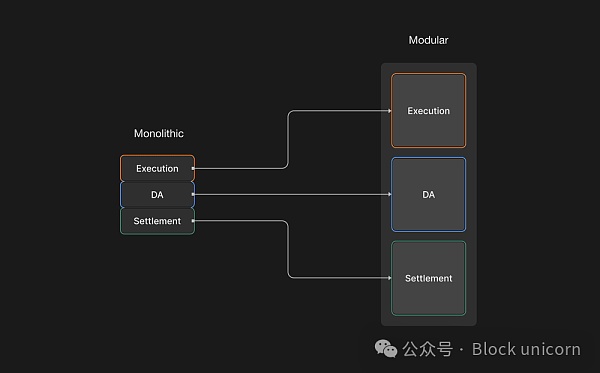
例如,Rollup通常有两个运行节点:一个用于执行Rollup的全节点,另一个用于结算+数据可用性(DA)的以太坊全节点。而validium可能会使用三个运行节点:一个用于执行Rollup的全节点,一个用于结算的以太坊全节点,以及一个用于DA的备用数据可用性全节点。
模块化将区块链的任务分配到至少两个全节点上。通过这种方式,模块化链可以利用多台计算机的计算能力来构建每个区块。
模块化是一种水平扩展的形式,对于思考区块链的可扩展性非常有用。

另一方面,大多数单体化阵营选择通过软件优化、实现并行虚拟机、数据管道、更快的网络协议和更强大的硬件来扩展。基本上,单体化链试图从一个全节点中提取最大的计算能力。
这是垂直扩展的一种形式。
批评者认为,这种方法趋向于集中化:如果依靠增加单个节点的计算能力来扩展,则不可避免地会遇到底层硬件的物理```html
近日,针对区块链技术的发展趋势展开了一场引人关注的讨论。
从技术实现角度来看,无论是单体化链还是模块化链,在扩展技术方面都展现出了无限的可能性。两者均可进行水平扩展和/或垂直扩展,这为其未来发展蓝图注入了新的活力。
对于模块化与单体化的辩论,始终围绕在水平与垂直扩展的框架内。从严格的技术角度来看,模块化倾向于水平扩展,而单体化则偏向于垂直扩展。
然而,随着模块化链的成功推出,额外的扩展优势已不再局限于“更加模块化”。如今,焦点已经转向链如何充分利用水平或垂直扩展技术。
运用水平与垂直思维模型,我们能够轻松推断每个链在此过程中所做的权衡,为未来发展提供了更清晰的路线图。
重新定义对话:水平 vs. 垂直扩展
在深入探讨水平 vs. 垂直扩展框架之前,重要的是要承认它的起源可以追溯到 20 世纪 70 年代,当时分布式计算研究为水平扩展概念奠定了基础。如今,所有的扩展技术都可以归类为水平或垂直扩展。
垂直扩展
通过增加每个节点的硬件利用率或硬件要求,垂直扩展成为了提高系统性能的有效途径。在区块链领域,这通常通过并行虚拟机等软件优化来实现。
一个典型的例子是 EVM 与 SVM。
EVM 按顺序执行事务,而 SVM 则是并行执行事务。通过利用更多的 CPU 核心,SVM 每秒可处理更多事务,这为区块链技术的性能提升提供了新的思路。需要注意的是,这种垂直扩展类型是 Eclipse L2 背后的基础。
然而,在权衡方面,垂直扩展受到可用硬件的限制,因硬件需求增加而趋于集中化,并且与水平扩展相比可扩展性较差。

水平扩展
水平扩展通过将工作负载分散到多个节点上来增加系统的可访问机器数量。正如前所述,模块化链本质上是将任务分配到多台机器上。此外,链通常还可以通过分片等技术实现更大程度的水平扩展。
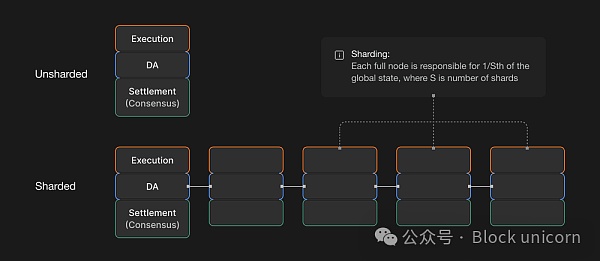
水平扩展与垂直扩展的区块链技术革新
近期,=nil; 基金会发布了一项重要技术进展,旨在推动以太坊网络的可扩展性和性能。这一技术称为 zkSharding,是去年11月推出的一项可验证的分片架构,为以太坊 Layer 2(L2)网络奠定了基础。
zkSharding的核心设计思想是将以太坊全局状态分割成多个分片,每个分片由去中心化委员会运行,负责构建区块和管理跨分片交易。此外,每个分片生成的有效性证明会发送到主分片进行聚合,然后在以太坊网络上进行发布和验证。这一架构通过两种方式发挥着水平扩展的能力:
首先,=nil;作为一个模块化区块链,充分利用了以太坊强大的共识机制和数据可用性,将任务分配到多个全节点上。
其次,=nil;作为一个分片区块链,将部分状态分布在众多全节点上。
这两种技术的结合有效减轻了单个机器的负担,并提高了整个网络的可扩展性。然而,水平扩展也面临着一些权衡,主要体现在网络和共识的复杂性以及机器或分片之间的异步通信。
追求以太坊可扩展性的终极目标
水平扩展和垂直扩展并非局限于模块化或单体化架构。水平与垂直扩展的对比为我们提供了更多探索新解决方案的空间,从而使模块化区块链更具可扩展性。
例如,一种选择是对模块化堆栈进行垂直扩展。其中一种常见方法是实现并行虚拟机,从而提高执行吞吐量。正如之前所述,Eclipse 正在利用 SVM 和其他 Rollups(如 Starknet)实现 BlockSTM,以实现并行化处理。
然而,垂直扩展始终受限于单台机器的物理极限,我们无法打破这些物理限制。
一种解决方案可能是通过分片实现水平扩展。当前的模块化设计才刚刚触及水平扩展的潜力。通过分片,我们可以利用任意数量机器的计算能力,而不仅仅是将任务分担给2-3台机器。
换句话说,许多机器可以并行运行相同类型的任务。这正是以太坊和 Celestia 希望通过 Danksharding 和数据分片实现的目标。但分片不仅局限于数据可用性层,还可以与执行相结合,如 =nil; L2 所示。
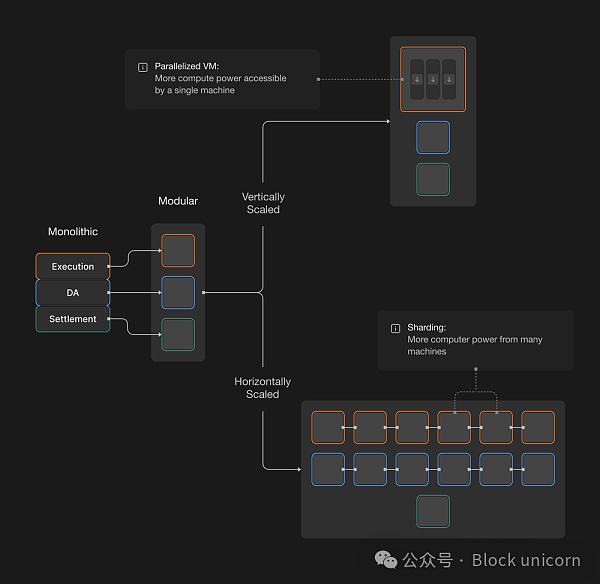
如果将通过模块化堆栈实现的水平扩展与分片提供的水平扩展相结合,我们将获得可用计算能力的大幅增加。然而,我们可以做得更好。
区块链可扩展性的最终目标将融合水平和垂直扩展,从而产生具有并行虚拟机的分片区块链。

在 =nil; 基金会,我们正在系统地朝着这个最终状态设计迈进。=nil; 的 L2 通过利用模块化、水平可扩展的架构(zkSharding)和垂直扩展的验证器实现(分片内并行化),采取了一条积极的扩展路线图。
因此,=nil; 的设计可以在不牺牲状态、流动性或用户碎片化的情况下实现全球规模。


Comparison between horizontal expansion and vertical expansion of blockchain scalability In recent years, with the rise of technology, the scalability of blockchain has been focused on the dispute between modularity and singleness. This binary opposition was originally a useful thinking mode to infer the scalability of blockchain, but now it can't meet our needs. So what alternatives are there? This paper will discuss horizontal expansion and vertical expansion as the basic framework of blockchain scalability and explain the adoption of horizontal expansion. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of vertical expansion modularity and singleness First, let's define a modular chain, which decomposes the core functions of a blockchain into different layers and integrates all core functions into a single interconnected layer. We can regard a layer as a machine singleness chain with one node to perform all tasks, while a modular chain has multiple full nodes to perform different tasks. For example, there are usually two running nodes, one for execution and the other for settlement of data availability. Taifang full node may use three running nodes, one for execution, one for settlement, and one for standby data availability. Full-node modularization distributes the tasks of blockchain to at least two full nodes. In this way, modular chain can use the computing power of multiple computers to build each block. Modularization is a form of horizontal expansion, which is very useful for thinking about the scalability of blockchain. On the other hand, most single camps choose. Choose the faster network protocol and more powerful hardware to expand the parallel virtual machine data pipeline through software optimization, and try to extract the maximum computing power from a whole node. This is a form of vertical expansion. Critics believe that this method tends to be centralized. If it relies on increasing the computing power of a single node to expand, it will inevitably encounter the new trend of physical horizontal and vertical expansion of the underlying hardware. Recently, the development trend of blockchain technology has been launched. There has been an interesting discussion. From the technical realization point of view, both the monomer chain and the modular chain have shown infinite possibilities in terms of expansion technology. Both of them can expand horizontally and or vertically, which has injected new vitality into their future development blueprint. The debate on modularity and singleness has always revolved around the framework of horizontal and vertical expansion. From a strict technical point of view, modularity tends to expand horizontally while singleness tends to expand vertically. However, with the modular chain, The successful introduction of additional expansion advantages is no longer limited to more modularity. Now, the focus has turned to how to make full use of horizontal or vertical expansion technology and use horizontal and vertical thinking models. We can easily infer that the trade-offs made by each chain in this process provide a clearer road map for future development, redefine the horizontal and vertical expansion of dialogue, and it is important to admit that its origin can be traced back to the 1990 s when distributed computing was studied as water. The concept of flat expansion has laid the foundation. Now all expansion technologies can be classified as horizontal or vertical expansion. Vertical expansion has become an effective way to improve the system performance by increasing the hardware utilization rate or hardware requirements of each node. In the blockchain field, this is usually achieved by software optimization such as parallel virtual machines. A typical example is to execute transactions in sequence, while parallel execution can handle more transactions per second by using more cores, which improves the performance of blockchain technology. L provides a new idea. It should be noted that this type of vertical expansion is the basis behind it. However, in terms of trade-off, vertical expansion is limited by available hardware, and tends to be centralized because of the increase in hardware requirements, and the scalability is poor compared with horizontal expansion. Schematic diagram of vertical expansion and horizontal expansion increase the number of accessible machines in the system by distributing the workload to multiple nodes. As mentioned above, the modular chain is essentially to distribute tasks to multiple machines. In addition, the chain can usually Realize a greater degree of horizontal expansion through fragmentation and other technologies. Schematic diagram of horizontal expansion Blockchain technical innovation of horizontal expansion and vertical expansion Recently, the Foundation released an important technical progress to promote the scalability and performance of the Ethereum network. This technology is called a verifiable fragmentation architecture launched last month, which laid the foundation for the Ethereum network. The core design idea is to divide the overall state of the Ethereum into multiple fragments. Fragments are run by the decentralization committee, which is responsible for building blocks and managing cross-fragment transactions. In addition, the validity certificate generated by each fragment will be sent to the main fragment for aggregation, and then published and verified on the Ethereum network. This architecture has the ability of horizontal expansion in two ways: first, as a modular blockchain, it makes full use of Ethereum's powerful consensus mechanism and data availability, and distributes tasks to multiple nodes; second, as a fragmented blockchain, it distributes some states in. The combination of these two technologies on many nodes effectively reduces the burden of a single machine and improves the scalability of the whole network. However, horizontal expansion also faces some trade-offs, which are mainly reflected in the complexity of the network and consensus, and the asynchronous communication between machines or segments, which pursues the ultimate goal of Ethernet scalability. Horizontal expansion and vertical expansion are not limited to modular or single architecture. The comparison between horizontal and vertical expansion provides us with more space to explore new solutions, so that modules can be Blockchain is more scalable. For example, one option is to vertically expand the modular stack. One common method is to implement parallel virtual machines to improve the execution throughput. As mentioned earlier, it is being used and implemented to achieve parallelization. However, vertical expansion is always limited by the physical limits of a single machine. We cannot break these physical limits. One solution may be to achieve horizontal expansion through fragmentation. The current modular design has just touched the potential of horizontal expansion. Fragmentation We can use the computing power of any number of machines instead of just sharing tasks with one machine. In other words, many machines can run the same type of tasks in parallel, which is exactly what Ethereum hopes to achieve through data fragmentation. However, fragmentation is not limited to the data availability layer, but it can also be combined with execution. As shown, if the horizontal expansion realized by modular stack is combined with the horizontal expansion provided by fragmentation, we will get a substantial increase in available computing power. However, we can do better. The ultimate goal of blockchain scalability will be to integrate horizontal and vertical expansion to produce parallel virtual expansion. 比特币今日价格行情网_okx交易所app_永续合约_比特币怎么买卖交易_虚拟币交易所平台
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。


















