解析RGB协议的设计与特点 以及面对的安全挑战
2023年下半年,各类 BTC 衍生协议的生态迅速发展。除了 Ordinals 协议与 BRC20 的再度爆火,Atomicals、Taproot Assets 等协议也受到了市场的广泛关注。
此前,Beosin 已为大家分析了几类 BTC 衍生协议的风险:《BTC生态爆火,解析其各类衍生协议的潜在机遇与风险》。本文 Beosin 将为大家详细讲解 BTC 生态非常重要的一类资产发行协议—— RGB 协议。
一、RGB 协议发展
RGB协议的作用是在闪电网络上为比特币增加了智能合约功能,基于零知识证明的状态通道协议,允许用户在链下进行隐私保护的交易。
RGB不是一个代币协议,但它具备发行与管理多种高度可扩展、可编程和保密的资产的能力,或可以在金融之外的许多其他行业中发挥重要作用。其协议的发展经历了多个重要阶段,从最初的构想到目前为比特币和闪电网络带来智能合约功能的RGB v0.10版本。
1. 2016年,Giacomo Zucco基于Peter Todd的理念,提出了RGB协议的初步构想。
2. 2017年,BHB Network推出了RGB协议原始版本,得到了Poseidon Group的支持。
3. 2019年,Maxim Orlovsky和Giacomo Zucco成立了LNP/BP标准协会,推动RGB向实际应用发展,Maxim Orlovsky博士开始重新设计RGB协议。
4. 2021年,该协会展示了RGB协议的图灵完备虚拟机(AluVM),RGB也开始在闪电网络上运行。
5. 2022年,推出了为Bitcoin和Lightning Network编写RGB智能合约的新语言Contractum及其新网站。
6. 2023年4月,发布了RGB v0.10版本,为比特币和闪电网络带来完全支持智能合约的功能,标志着RGB协议进入最为重要的发展阶段。
二、RGB 协议设计逻辑
RGB协议的核心思想是围绕着共识和链下数据存储构建的。
首先,分布式系统最重要的价值是共识的维护,利用比特共识层只需要保留对账本事件的简短的加密提交(cryptographic commitments),证明特定数据存在但不透露实际数据内容的技术,通常通过哈希函数实现,仅在链上存储这些提交去保证数据的真实性和完整性,进而减少了链上数据的负担。
RGB设计的账本数据存储在链下,也就是说所有的合约数据和状态转换都保留在链下,而不是在区块链上。利用单次使用密封和状态转换来追踪和验证智能合约的状态,在不将全部数据存储在链上的情况下,有效地处理和验证智能合约的状态和交易。
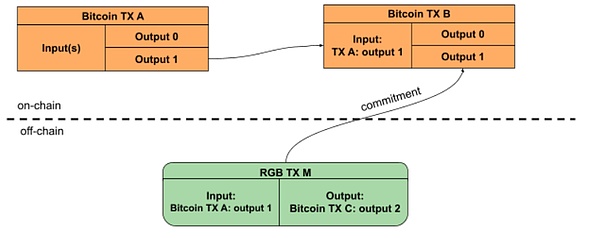
RGB的基础层是比特币区块链,包括Nakamoto PoW共识和交易账本。虽然不需要在链上存储任何数据,但仍需要遵循现有的基础设施,并利用比特币交易作为这些承诺的存储。
2.1 客户端验证
RGB智能合约在客户端验证模式下,所有数据都将保留在比特币交易之外,例如比特币区块链或闪电网络通道状态,使该系统能够在闪电网络之上运作,也为高级别的协议可扩展性和隐私提供了基础。
2.2 RGB 智能合约
RGB 智能合约的基本构成包括 Genesis(创世)、State(状态)和 Transitions(转换),每部分承担着不同的功能和角色:
Genesis(创世)
Genesis是智能合约的初始化声明,它定义了合约的基本属性和规则。这包括合约的类型、目的和任何初始设置。在代码中,genesis部分定义了合约的起始点,比如在一个身份验证合约中,它可以指定初始的身份信息。
State(状态)
State代表了合约在任何给定时刻的当前状态,是合约数据的实时快照,包括了所有的变量值和资产信息。
Transitions(转换)
Transitions是定义从一个状态到另一个状态转换的规则。这些规则决定了状态如何根据合约逻辑发生变化。op Revocation和op Transfer是转换的例子,它们定义了如何从一个Identity状态转移到另一个,或者如何在代币之间进行转移。
通过这三个组成部分提供了一种方式来定义和执行各种操作和协议。Genesis设定了基础规则和参数,State维护了合约的当前信息,而Transitions则规定了状态之间的变化逻辑,共同构成了RGB智能合约的核心架构。
2.3 一次性密封(single-use-seals)
为了确保安全和高效地管理资产转移,同时保护用户隐私。RGB协议使用了“single-use-seals”的方法,这种方法允许将资产(如代币)与比特币的一个特定交易输出绑定,使得每次资产转移都需要“打开”一个旧的密封并“创建”一个新的密封。一次性封装用于代表资产的所有权或合约状态。每次状态转移或交易发生时,相关的封装会被关闭并创建新的封装,这样做的好处是,每个密封只能使用一次,从而防止了资产的重复使用或双重支付,确保了交易的安全性,进而确保资产的转移不可篡改。
同时,由于这些操作是在客户端进行的,而不是全部存储在区块链上,因此大大增强了用户的隐私保护,并减少了对区块链空间的占用,提高了整体网络的效率和可扩展性。
single-use-seals的逻辑步骤:
1. 每个RGB合约的开始都是一个创世操作,这里会定义初始状态和相关的一次性封装,代表了合约中定义的资产或权限的初始分配。
2. 在合约中,状态(State)被用来表示当前资产或权限的配置。每个状态都与一个一次性封装相关联,表示当前的所有权或权限。
3. 当需要转移或改变资产或权限时,涉及到状态的转换(Transitions)。这个过程包括关闭当前的一次性封装(表示旧的状态)并创建一个新的封装(代表新的状态)。
4. 关闭一个封装涉及到验证其完整性并标记为已使用,以防止重复使用。然后,基于合约规则创建一个新的封装,以代表新的状态。
5. 交易发生时,合约参与者需要验证相关的一次性封装是否有效,以确保交易的合法性。这个验证过程是自动的,由RGB节点和参与的钱包协作完成。
三、RGB 协议的特性
RGB的特性体现在RGB智能合约的创新,下面为大家介绍一些关键点:
1. 模式(Schema)概念
RGB协议采用了模式(Schema)的概念,类似于面向对象编程中的类。模式用于定义RGB资产的标准,便于钱包、交易所、浏览器和BTC节点支持RGB资产。在这个框架中,一个具体的RGB合约是某个模式的实例,由该模式的构造函数(“创世操作”)创建。这种方法分离了合约开发者(模式开发者)和合约发行者的角色,使得后者无需具备编程或安全知识。
2. AluVM虚拟机
RGB协议还引入了AluVM虚拟机,这是一个图灵完备的虚拟机,类似于以太坊的EVM。它可以执行几乎所有类型的计算,但受到操作步骤数的限制。AluVM通过累积的计算复杂性度量来限制计算,类似于以太坊的gas消耗机制。
3. 合约定义示例
在合约定义方面,RGB协议使用特定的数据类型,如PgpKey,这些类型不是合约的直接组成部分,而是可以被多个合约共享。合约的状态和操作,如Identity和Revocation,被定义为合约状态的组成部分和可能的状态转换。
4. 合约实例和状态转换
合约实例化是通过将模式应用于具体情况来完成的,例如,meSatoshiNakamoto实现了DecentralizedIdentity模式,定义了初始状态并将其分配给一次性密封。状态转换,如通过Revocation操作,涉及更新身份并将其分配给新的一次性密封。
5. 扩展合约功能
RGB协议允许扩展合约功能,如添加IOU(I OWE YOU)代币,在合约中表现为可拥有的状态IOYTokens。此外,还有全局状态,如IOYTicker和IOYName,这些是合约的全局属性,不被任何一方直接拥有。
6. 状态扩展的概念
状态扩展的概念允许公众参与合约的特定逻辑部分,如通过声明Burn的方式。状态扩展操作允许任何人在不进行链上承诺的情况下创建状态扩展,类似于未打包进区块的比特币交易。
7. 合约接口(Contract Interface)
标准化通信:合约接口提供了与RGB节点交流的标准方式,要求它返回有语义意义的状态并创建操作。
类似于以太坊的ERC标准:这些接口类似于以太坊的ERC标准,通用的接口被称为"RGBxx",作为独立的LNP/BP标准定义。
8. 创建通用代币接口示例
接口定义: 定义了全局状态(如Ticker和Name)和拥有的状态(如Inflation和Asset),以及操作(如Issue和Transfer)。
接口实现:实现接口时,将特定模式的状态和操作与接口绑定。例如,FungibleToken接口为DecentralizedIdentity模式实现了全局和拥有的状态绑定。
四、RGB 协议应用
金融方面的应用:
1. 用于创建代表公司或项目股份的通证,集中发行但通过去中心化的方式交易,提高市场流动性和透明度。
2. 管理贷款和债券,通过智能合约实现自动化的贷款和债券发行和还款。
3. 创建运行在闪电网络上的稳定币,并将这些稳定币可以作为支付手段。
4. 创建去中心化交易所(DEX)。
5. 应用例如算法过度抵押的稳定币等AMM解决方案,为市场提供流动性和稳定性。
非金融领域的应用:
1. 用于管理自主身份解决方案,使个人能够控制和管理他们的数字身份信息。
2. 创建一个去中心化的全球名称注册系统,以便人们能够注册和管理域名和其他网络标识符。
3. 管理数字内容的所有权和许可权,包括版权和许可证。
4. 用于通证化艺术品,为艺术家和收藏家提供了一种新的数字所有权和交易平台。
5. 管理DAOs,以实现去中心化的决策和治理。
6. 用于创建可证明和可验证的审计日志系统,以提高企业和项目的透明度和可信度。
五、当前 RGB 协议的风险
1. 不稳定性
当前的RGB协议是首个完全支持智能合约的版本,后续RGB协议可能会进行一些重大的更新或者修改,这会导致目前开发的合约无法在后续版本安全、稳定地运行。RGB的客户端验证节点也仍在更新中,还未有稳定的版本。
2. 复杂性
RGB协议的设计和实现都相当复杂,基于RGB协议开发的智能合约需要考虑很多RGB协议的特性。例如,基于RGB协议发行的代币,如果交易失败或是没有得到RGB节点的确认,那么这些代币不属于任何UTXO,相当于被销毁了,开发者和项目方需要仔细考虑这类情况对于项目代币经济的影响。
总结
RGB协议目前仍处于非常早期的阶段。RGB协议通过其独特的模式定义、AluVM虚拟机、灵活的合约状态管理和扩展机制,展现了其在BTC智能合约领域的创新,支持在比特币网络和闪电网络上进行多种资产的发行和转移。但目前RGB协议与闪电网络还未完全兼容,智能合约的开发和运行未有安全保障,用户使用RGB协议时需留意风险。
In the second half of 2006, the ecology of various derivative agreements developed rapidly, except for the agreement and the re-explosion of agreements, which also attracted wide attention in the market. Previously, the risks of several derivative agreements were analyzed, and the potential opportunities and risks of various derivative agreements were analyzed. This paper will explain in detail a kind of asset issuance agreement, which is very important in ecology. The role of the agreement development agreement is to add intelligent contract function to Bitcoin on the lightning network. The state channel agreement based on zero knowledge proof. The transaction that allows users to protect their privacy under the chain is not a token agreement, but it has the ability to issue and manage a variety of highly scalable, programmable and confidential assets, or it can play an important role in many other industries besides finance. The development of the agreement has gone through many important stages, from the initial idea to the current version that brings smart contract functions to Bitcoin and lightning networks. The initial idea of the agreement was put forward in, and the original version of the agreement was launched in. And set up a standards association to promote the development of practical applications, and Dr. began to redesign the protocol in. The association showed the Turing complete virtual machine of the protocol and began to run on the lightning network. In, a new language for writing smart contracts and its new website were launched, and a version was released in. The function of fully supporting smart contracts for Bitcoin and lightning networks marked that the protocol entered the most important development stage. The core idea of protocol design logic protocol was built around consensus and offline data storage. First of all, the most important value of distributed system is the maintenance of consensus. By using the bit consensus layer, only short encrypted submissions of account book events are needed to prove the existence of specific data without revealing the actual data content. Usually, these submissions are stored only on the chain through hash function to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the data, thus reducing the burden of data on the chain. The designed account book data is stored under the chain, that is to say, all contract data and state transitions are kept under the chain rather than in the blockchain. Tracking and verifying the status of smart contracts by single-use sealing and state transition is the basic layer for effectively processing and verifying the status and transactions of smart contracts without storing all the data on the chain. Bitcoin blockchain includes consensus and transaction books. Although it is not necessary to store any data on the chain, it is still necessary to follow the existing infrastructure and use bitcoin transactions as the storage of these commitments. In the client verification mode, all data will be retained. Beyond bitcoin transactions, such as bitcoin blockchain or lightning network channel state, the system can operate on lightning network, and it also provides a foundation for high-level protocol scalability and privacy. The basic components of smart contracts include creation state and conversion, and each part bears different functions and roles. Creation is the initialization statement of smart contracts, which defines the basic attributes and rules of the contracts, including the types, purposes and any initial settings of the contracts. The contracts are partially defined in the code. For example, in an authentication contract, it can specify the initial identity information state, which represents the current state of the contract at any given moment. It is a real-time snapshot of the contract data, including all variable values and asset information conversion. These rules determine how the state changes according to the contract logic and are examples of conversion. They define how to transfer from one state to another or how to transfer between tokens. These three components provide a way to define and execute various operations and protocols, set basic rules and parameters, maintain the current information of the contract, and stipulate the logic of changes between states, which together constitute the core structure of the smart contract. One-time sealing is a method used in the protocol to ensure safe and efficient management of asset transfer and protect user privacy. This method allows assets such as tokens to be bound to a specific transaction output of Bitcoin so that every asset transfer is required. It is necessary to open an old seal and create a new one-time seal to represent the ownership or contract status of assets. Every time a state transfer or transaction occurs, the relevant seal will be closed and a new seal will be created. The advantage of this is that each seal can only be used once, thus preventing the reuse or double payment of assets, ensuring the security of transactions and ensuring that the transfer of assets cannot be tampered with. At the same time, because these operations are carried out at the client, they are not all stored in the blockchain. This greatly enhances the privacy protection of users, reduces the occupation of blockchain space, and improves the efficiency and scalability of the whole network. The beginning of each contract is a creation operation. Here, the initial state and related one-time packages represent the initial allocation of assets or rights defined in the contract. In the contract, the state is used to represent the configuration of current assets or rights, and each state is associated with a one-time package to represent the current ownership or rights when it needs to be transferred. When changing assets or permissions, it involves state transition. This process includes closing the current one-time package to represent the old state and creating a new package to represent the new state. Closing a package involves verifying its integrity and marking it as used to prevent reuse, and then creating a new package to represent the new state based on contract rules. When a transaction occurs, contract participants need to verify whether the related one-time package is valid to ensure the legitimacy of the transaction. This verification process is automatic. The characteristics of the three protocols are embodied in the innovation of smart contracts. Here, we will introduce some key patterns. The conceptual protocols adopt the concept of patterns, which is similar to the class patterns in object-oriented programming. It is convenient for wallet exchange browsers and nodes to support assets. In this framework, a specific contract is an instance of a pattern created by the constructor of the pattern. This method separates the contract developers from the pattern developers. And the role of contract publisher makes the latter not need to have programming or security knowledge. The virtual machine protocol also introduces a virtual machine, which is a Turing complete virtual machine similar to Ethereum. It can perform almost all kinds of calculations, but is limited by the number of operation steps. The calculation is limited by the cumulative calculation complexity measure. The contract definition example shows that in the contract definition, the protocol uses specific data types, such as these types are not the direct components of the contract, but can be shared by multiple contracts. The state and operation of the contract, such as sum, are defined as the components and possible states of the contract state. 比特币今日价格行情网_okx交易所app_永续合约_比特币怎么买卖交易_虚拟币交易所平台
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。


















