在央行数字货币、稳定币和狭义银行新世界中的货币政策实施指南
来源:FEDS,作者:James A. Clouse
2024年1月,Federal Reserve Board, Washington, D.C.在FEDS发布了《在央行数字货币、稳定币和狭义银行新世界中的货币政策实施指南》(A Field Guide to Monetary Policy Implementation Issues in a New World with CBDC, Stablecoin, and Narrow Banks)一文,该文在新政策工具、技术进步和监管发展的背景下试图讨论金融市场的结构演变对货币政策实施的传导影响。
本文作者在前人研究的基础上结合Tobin(1969)、Gurley and Shaw(1960)等知名学者从货币理论和货币政策视角对银行业的研究,建立了一个可以分析银行和非银行部门的监管发展与货币政策实施之间的量化框架。该框架描述了金融市场竞争模型中所有金融工具的一组相互关联的供求曲线,并考虑了金融中介机构的投资组合分配成本和资产负债表成本,此外特别讨论了包括零售和批发在内的央行数字货币(CBDC)、稳定币和狭义银行提供的存款的影响,以及这些结构性变化会如何影响利率以及资产负债表的规模和结构。本文得出,美联储或其他金融中介机构引入新的固定利率资产会对均衡利率和金融中介模式产生重大影响,也可能影响货币政策工具的效力。当新的金融资产是现有金融资产的近似替代品时,这些影响最为明显。
基准模型
基于Chen等人(2014 年)的基准模型涉及多个部门,包括家庭、银行、非银行、企业、政府和外国部门,本文提出的模型沿袭了托宾(1969)的思路,基于一个简单的投资组合优化框架,推导出各部门对金融资产的需求。该框架的关键要素是投资组合习惯,它定义了家庭和金融中介机构的基准目标资产和负债分配。家庭和金融中介机构可以偏离这些投资组合习惯分配,但这样做会产生投资组合成本。除投资组合构成成本外,金融中介机构还面临扩大资产负债表规模的成本。
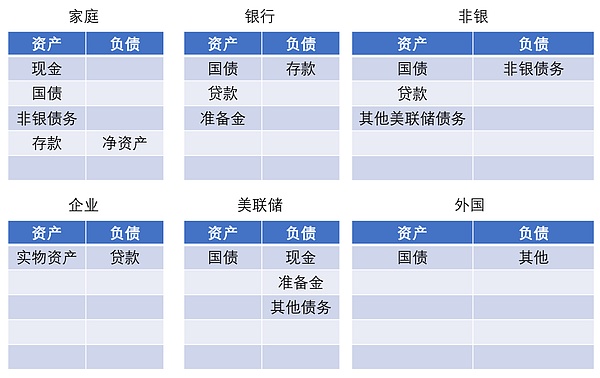
图表 1 基准模型中的金融市场结构
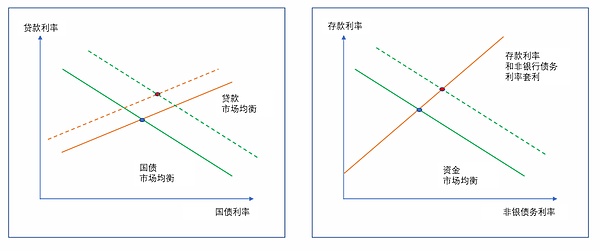
本文描述的均衡利率可以简化为两个方面:一个描述与贷款市场均衡一致的贷款利率和国债利率组合,另一个描述与国债市场均衡一致的贷款利率和国债利率组合。
如图2左侧的橙色线所示,贷款市场均衡曲线是向上倾斜的(在其他条件不变的情况下,国库券利率越高,意味着贷款利率必须越高,中介机构才愿意提供任何给定数量的贷款)。国债市场均衡曲线(绿线)一般是向下倾斜的(在其他条件不变的情况下,较低的贷款利率会导致贷款市场上更多的借贷,需要较高的国债利率来吸引清理国债市场所需的额外资金)。
而存款和非银行债务均衡利率也可以在基准模型的假设下通过图2右边的橙色线表示出来。存款利率和非银行债务利率之间的利差反映了储备金管理利率和其他美联储负债管理利率之间的差距,也反映了家庭对存款和非银行债务的相对需求。资金市场均衡关系,即图中的绿线,描述了家庭投资于存款和非银行债务的愿望与银行和非银行提供的存款和非银行债务供应之间的平衡。这条曲线的位置受到银行和非银行加权平均资产回报率以及家庭投资组合中与存款和非银行债务竞争的资产利率的强烈影响。
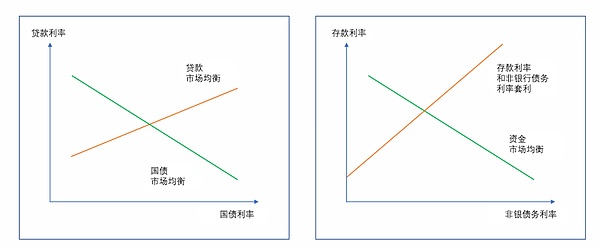
图表 2 基准模型中的均衡
此外由于假定家庭对其希望持有的金融资产有相对较强的习惯,家庭偏好在很大程度上决定了金融中介机构的相对规模。特别是,银行、非银行和美联储资产负债表的相对规模主要分别由家庭对存款、非银行债务和实物货币的相对需求规模所驱动。银行和非银行的资产构成在很大程度上反映了这些部门的习惯。
考虑央行数字货币、稳定币和狭义银行的三种基准模型变体
第一种变体考虑的是包含零售和批发中央银行数字货币。在该模型中,只有家庭可以投资零售中央银行数字货币,而银行和非银行金融机构可以投资批发中央银行数字货币。
第二种变体是在模型中引入所谓的稳定币。稳定币由狭义的非银行机构发行,仅由家庭持有。
第三种变体考虑了所谓的狭义银行的作用,即发行存款并仅以储备金的形式持有资产。
举例来说,图3说明了在引入一种新的有息资产对家庭存款需求产生的替代效应。左边部分显示最初的家庭存款曲线是向上倾斜的,存款利率绘制在纵轴上。当存款利率等于投资组合参考利率时,家庭对存款的需求正好等于存款的习惯水平。右边部分显示了引入一种新的生息资产对该存款曲线的假设影响。如果新的金融资产吸引了以存款为代价的惯常需求水平,那么新的惯常存款水平就会下降,如黑线向绿线的移动所示。如果新的金融资产有利息,投资组合基础利率也会发生变化。图中显示了当投资组合参考利率从绿线上升到红线时的影响。最后,根据作者对习惯的偏离成本的假设,如果存款习惯水平下降,存款线的斜率就会变陡,从红线到蓝线的旋转显示了这一点。所有这些类型的替代效应都在模型中发挥着重要作用。
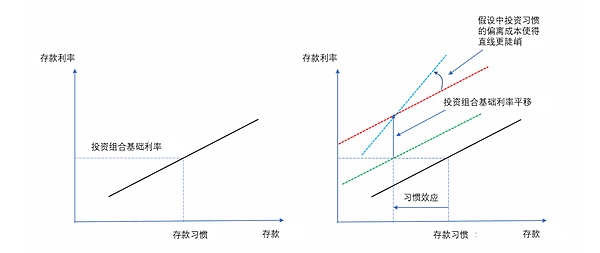
图表 3引入新金融资产的影响
具体而言,文章认为中央银行数字货币是一种新的金融资产,并对基准模型的第一种变体进行研究,记零售和批发中央银行数字货币分别为R_CBDC和W_CBDC。其中,R_CBDC仅由家庭持有,是一种新的金融资产,可作为投资工具,美联储也有相应的新负债。假设家庭对R_CBDC有一种“习惯”,类似于对其他金融资产的“习惯”。在模型中引入R_CBDC还需要一个新的美联储负债管理利率,????_???????,文章假定该利率为零,以匹配实物货币的假定利率并假设对R_CBDC的习惯最初完全以牺牲对实物货币的习惯为代价,同样,本文假设W_CBDC的利率设定在与金融中介机构持有的准备金或其他美联储负债相当的水平。
文章研究结果表明,美联储管理的所有利率——实物货币的名义利率、零售央行数字货币、储备、其他美联储负债和批发央行数字货币的利率——以及均衡贷款利率的同等提高,导致所有市场利率一对一地传递。在这种情况下,所有的利差都不受影响,所以均衡量也不受这种变化的影响。扩展模型中的均衡在很大程度上取决于对家庭和金融中介机构“习惯”转变的假设。一般来说,如果零售或批发央行数字货币的投资组合习惯是以牺牲另一种美联储负债或国债的习惯为代价的,那么模型中的均衡相对于基准模型基本上是不变的。
具体而言,零售央行数字货币利率的上升会对利率产生上行压力。如图4所示,R_CBDC利率的上升使贷款市场均衡曲线向上移动,导致贷款利率上升,国债利率下降。这一变化还使融资市场均衡线向外移动,导致存款利率和非银行债务利率同样上升。R_CBDC利率的上升导致家庭从其他资产转移到R_CBDC。由此导致的存款和非银行债务市场中介机构可用资金的减少,导致银行和非银行机构缩减资产规模,所有资产类别都出现了这种下降。对贷款总量有轻微的负面影响。在美联储的资产负债表上,储备、批发央行数字货币、其他美联储负债和货币都在下降,而零售央行数字货币则在增加。总的来说,美联储资产负债表的规模增加了。
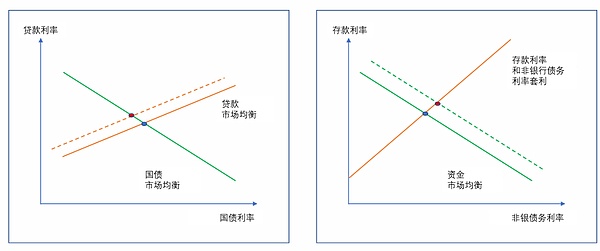
图表 4 零售中央银行数字货币加息产生的影响
对于批发型而言,因为批发央行数字货币(W_CBDC)由银行和非银行机构共同持有。因此,W_CBDC利率的上升直接影响到银行和非银行资产配置。W_CBDC利率上升对利率的影响如图5所示,与基准模型中准备金利率和其他美联储负债利率平行上升的情况类似。如左图所示,W_CBDC利率的上升使贷款市场均衡曲线上移并向左移动,同时也拉升了国债市场均衡曲线。后一种效应源于一种假设,即W_CBDC利率成为外国部门国债需求曲线上“基准”利率的一部分。净效应是国债利率和贷款利率都在上升。这些增长导致银行和非银行机构对资金的需求增加——右图中融资市场均衡线向外移动表明了这一点:导致存款和非银行机构债务利率上升。
图表 5批发中央银行数字货币加息产生的影响
结论与建议
本文的分析指出了技术、监管和金融结构的演变可能与货币政策的实施和传导相互作用的几种途径。近年来,美联储以计息储备金和固定利率隔夜逆回购协议的形式引入固定利率资产,为政策实施创造了强有力的新工具,而这些工具对于在充裕储备制度下维持高储备金水平的环境中是有效控制利率的关键所在。因此当美联储(以零售和批发央行数字货币的形式)或专业金融中介机构(以稳定币或狭义银行提供的存款的形式)引入额外的固定利率金融资产,会与现有市场和机构相互作用,影响政策实施和传导的重要方面。当新的固定利率工具成为现有金融工具的近似替代品时,这些影响最为明显。
以下为文章部分截图

The source author published a guide to the implementation of monetary policy in the new world of the central bank, digital currency's stable currency and narrow banks in June. This paper tries to discuss the transmission influence of the structural evolution of financial markets on the implementation of monetary policy under the background of new policy tools, technological progress and regulatory development. On the basis of previous studies, the author has established a monetary policy that can analyze the regulatory development and monetary politics of banks and non-banking sectors from the perspective of monetary theory and monetary policy. The quantitative framework between policy implementation describes a set of interrelated supply and demand curves of all financial instruments in the financial market competition model, and considers the portfolio allocation cost and balance sheet cost of financial intermediaries. In addition, the influence of the central bank, including retail and wholesale, the digital currency stable currency and the deposits provided by narrow banks, and how these structural changes will affect interest rates and the size and structure of the balance sheet are discussed. The introduction of new fixed-rate assets by intermediaries will have a great impact on the equilibrium interest rate and the financial intermediation model, and may also affect the effectiveness of monetary policy tools. When the new financial assets are approximate substitutes for the existing financial assets, these effects are most obvious. The benchmark model based on the equal-year benchmark model involves many departments, including family banks, non-banks enterprises, governments and foreign departments. The model proposed in this paper follows Tobin's idea and deduces the investment of various departments based on a simple portfolio optimization framework. The key element of this framework is portfolio habit, which defines the benchmark target of households and financial intermediaries, the distribution of assets and liabilities. Households and financial intermediaries can deviate from the customary distribution of these portfolios, but doing so will generate portfolio costs, in addition to the cost of portfolio composition, financial intermediaries will also face the cost chart of expanding the balance sheet size, and the financial market structure in the benchmark model. The equilibrium interest rate described in this paper can be simplified into two aspects, one is description and loan. Another description of the combination of loan interest rate and national debt interest rate is the combination of loan interest rate and national debt interest rate that is consistent with the national debt market equilibrium. As shown by the orange line on the left, the loan market equilibrium curve is inclined upward. Under other conditions unchanged, the higher the treasury bill rate means, the higher the loan interest rate must be. Intermediaries are willing to provide any given amount of loans. The green line of the national debt market equilibrium curve is generally inclined downward, and the loan interest is lower under other conditions unchanged. The interest rate will lead to more loans in the loan market, which requires higher interest rate of government bonds to attract additional funds needed to clean up the government bond market, and the equilibrium interest rate of deposits and non-bank debts can also be shown by the orange line on the right side of the figure under the assumption of the benchmark model. The spread between the deposit interest rate and the non-bank debt interest rate reflects the gap between the reserve management interest rate and other Fed debt management interest rates, and also reflects the relative demand of households for deposits and non-bank debts. The capital market equilibrium relationship is shown in the figure. The green line in the middle describes the balance between the desire of households to invest in deposits and non-bank debts and the supply of deposits and non-bank debts provided by banks and non-banks. The position of this curve is strongly influenced by the weighted average return on assets of banks and non-banks and the interest rate of assets competing with deposits and non-bank debts in the family portfolio. In addition, the balance in the benchmark model is largely determined by the assumption that families have relatively strong habitual family preferences for the financial assets they want to hold. The relative scale of financial intermediaries, especially the balance sheets of banks, non-banks and the Federal Reserve, is mainly driven by the relative demand scale of households for deposits, non-bank debts and physical currency, which largely reflects the habits of these departments. The first variant considers the three benchmark model variants of the central bank, digital currency stable currency and narrow bank. The first variant considers the retail and wholesale central bank, digital currency. In this model, only families can. Invest in digital currency, the retail central bank, while banks and non-bank financial institutions can invest in digital currency, the wholesale central bank. The second variant is to introduce the so-called stable currency into the model. The stable currency is issued by non-bank institutions in a narrow sense and only held by households. The third variant considers the role of the so-called narrow bank, that is, issuing deposits and holding assets only in the form of reserves. For example, the figure shows the substitution effect of introducing a new interest-bearing asset on household deposit demand. The left part shows the most. The initial household deposit curve is an upward sloping deposit interest rate plotted on the vertical axis. When the deposit interest rate is equal to the reference interest rate of the portfolio, the household demand for deposits is just equal to the customary level of deposits. The right part shows the hypothetical influence of introducing a new interest-bearing asset on the deposit curve. If the new financial asset attracts the customary demand level at the expense of deposits, the new customary deposit level will drop as shown by the movement of the black line to the green line. If the new financial asset has an interest-bearing portfolio, The base interest rate will also change. The diagram shows the impact when the reference interest rate of the portfolio rises from the green line to the red line. Finally, according to the author's assumption that the habit deviates from the cost, the slope of the deposit line will become steeper if the deposit habit level drops. The rotation from the red line to the blue line shows this point. All these types of substitution effects play an important role in the model. The diagram shows the impact of introducing new financial assets. Specifically, the article thinks that the central bank digital currency is a new financial asset and has a negative impact on the base. The first variant of quasi-model is studied. digital currency, the central bank of retail and wholesale, is a new financial asset, which is only held by families. The Federal Reserve also has corresponding new liabilities. It is assumed that families have a habit similar to that of other financial assets, and a new Federal Reserve debt management interest rate is needed to introduce into the model. The article assumes that the interest rate is zero to match the assumed interest rate of physical currency, and assumes that the right habit is completely at the expense of physical currency at first. Similarly, the interest rate assumed in this paper is set at the same level as the reserves held by financial intermediaries or other Fed liabilities. The research results show that all interest rates managed by the Fed, nominal interest rates of physical money, retail central bank digital currency reserves other Fed liabilities, interest rates of wholesale central bank digital currency and the equal increase of balanced loan interest rates lead to the one-to-one transmission of all market interest rates. In this case, all spreads are not affected, so all spreads are not affected by this change. The equilibrium in the extended model depends to a large extent on the change of habits of families and financial intermediaries. 比特币今日价格行情网_okx交易所app_永续合约_比特币怎么买卖交易_虚拟币交易所平台
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。



















