如何设计更好的链上治理?Futarchy模型的探索与应用
作者:Malte Kliemann 来源:coindesk 翻译:善欧巴,比特币买卖交易网 链上治理的话题一直存在争议。虽然链下治理通常被认为是笨拙的,但链上治理允许开发人员构建日益复杂的协议,允许用户左右网络的方向。但这些本质上都是游戏,如果配置错误或提供错误的激励措施,可能会导致整个链条走向灾难。 在“什么是 Futarchy?——交易未来”,Gnosis 联合创始人 Freiderike Ernst 强调了链上投票的标准方法。由于“每人一票”范式很容易受到无许可网络上的Sybil 攻击(一个人可以将其资金分散到多个账户并投出多票),因此用户的投票权通常按其持有的代币数量进行加权。彩票和代币管理注册中心使用相同的方法来避免女巫攻击。 Robin Hanson 提出了一种名为futarchy的新治理模型,其中决策不是基于投票,而是基于组织福利措施的预测市场结果,该福利措施是网络增长或消亡的指标。市场参与者将押注福利措施的未来价值。 投注通常使用结果代币来实现,每个结果代币代表市场的一个特定结果,其货币价值由最终的福利指标决定。好的预测会得到奖励,坏的预测会导致损失。 使用结果代币,参与者甚至可以根据政策的实施来押注福利措施的价值。例如,参与者可以进行投注,如果政策执行并且福利措施增加一定数量,则支付利润,但如果政策不执行,则无效。 对于一家选择股价作为福利衡量标准并考虑解雇首席执行官的上市公司,其结果是该组织获得两个预测,即首席执行官被解雇时的未来股价和首席执行官被解雇时的未来股价。被保留。从下图可以看出: 有了futarchy,就会实施导致最高可能福利措施的决策。由于最终 CEO 被解雇的股价预测高于 CEO 留任的预测,因此 CEO 被解雇。这消除了决策过程中的所有情感,使组织能够根据通常所说的“群体的智慧”做出理性决策,以提高其价值观。 实施做市商来促进参与者之间的交易带来了一些挑战。如果我们想使用 futarchy 来评估更复杂的突发事件,市场很快就会增加到数以万计的代币。在这里,“薄弱市场问题”浮出水面:没有足够的参与者来正确纠正这么多结果的概率。自然的解决方案是自动化做市商(AMM)。 一个简单的解决方案是对数市场评分规则的成本函数实现。不幸的是,这种实施不允许流动性发生临时变化,通常会导致市场要么太浅而无法容纳所有参与者,要么太深而无法实际产生有意义的结果。流动性敏感的对数市场评分规则(LS-LMSR)缓解了这个问题,但该解决方案引入了新的缺陷,其中最严重的是套利漏洞,该漏洞出现在除 LMSR 之外的所有评分规则做市商中。 Balancer等加密货币中流砥柱的恒定函数做市商(CFMM)通过允许 LP 动态存入和提取流动性来更好地处理流动性方面,并且对加密货币本地人来说更熟悉,但也遇到了与 LS-LMSR 相同的问题。然而,事实证明,在预测市场期间,Gnosis 似乎找到了LMSR 的 CFMM 实现,它结合了两全其美的优点。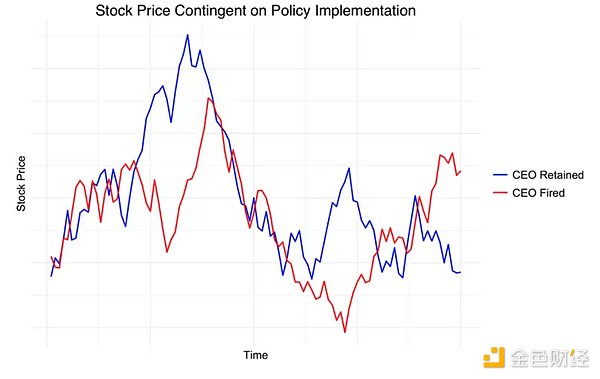
预测市场的做市商
The topic of online governance of good Ouba bitcoin trading has always been controversial. Although offline governance is usually considered clumsy, online governance allows developers to build increasingly complex protocols and users to control the direction of the network, but these are essentially games. If the configuration is wrong or the wrong incentives are provided, the whole chain may lead to disaster. What is the future of trading? The co-founders emphasized the standard method of online voting because the paradigm of one vote per person is easy. Attacked by an unlicensed network, a person can spread his funds to multiple accounts and cast multiple votes, so the voting rights of users are usually weighted according to the number of tokens they hold. Lottery and token management registration centers use the same method to avoid witch attacks, and propose a new governance model called "Witch Attack", in which decision-making is not based on voting, but on predicting the market outcome of organizational welfare measures, which is an indicator of the growth or death of the network. Market participants will bet on the future of welfare measures. Value betting usually uses outcome tokens to realize that each outcome token represents a specific outcome of the market, and its monetary value is determined by the final welfare index. Good predictions will be rewarded, and bad predictions will lead to losses. Participants can even bet on the value of welfare measures according to the implementation of policies. For example, participants can make bets. If the policies are implemented and the welfare measures increase by a certain amount, they will pay profits, but if the policies are not implemented, they will be invalid. For a family, it is a blessing to choose the stock price. As a result, the organization obtains two forecasts, that is, the future share price when the CEO is fired and the future share price when the CEO is fired. As can be seen from the following figure, the decision that leads to the highest possible welfare measures will be implemented, because the stock price forecast that will eventually be fired is higher than the forecast of staying, which eliminates all emotions in the decision-making process and enables the organization to make rationality according to the wisdom of the group. Making decisions to improve their values, forecasting market makers, and implementing market makers to promote transactions between participants have brought some challenges. If we want to use them to evaluate more complex emergencies, the market will soon increase to tens of thousands of tokens, where weak market problems surface and there are not enough participants to correctly correct the probability of so many results. The natural solution is to automate market makers. Unfortunately, a simple solution is to realize the cost function of logarithmic market scoring rules. This implementation does not allow temporary changes in liquidity, which usually leads to the market being either too shallow to accommodate all participants or too deep to actually produce meaningful results. The liquidity-sensitive logarithmic market scoring rules have alleviated this problem, but the solution has introduced new defects, the most serious of which is the arbitrage loophole, which appears in all scoring rules except market makers, the mainstay of cryptocurrency, and the constant function market makers allow dynamic deposit and withdrawal of liquidity. Dealing with liquidity better and being more familiar to cryptocurrency locals, but also encountering the same problems. However, it turns out that it seems to have been found during the market forecasting period, which combines the advantages of the best of both worlds. 比特币今日价格行情网_okx交易所app_永续合约_比特币怎么买卖交易_虚拟币交易所平台
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。